How to use the SUMPRODUCT function
What is the SUMPRODUCT function?
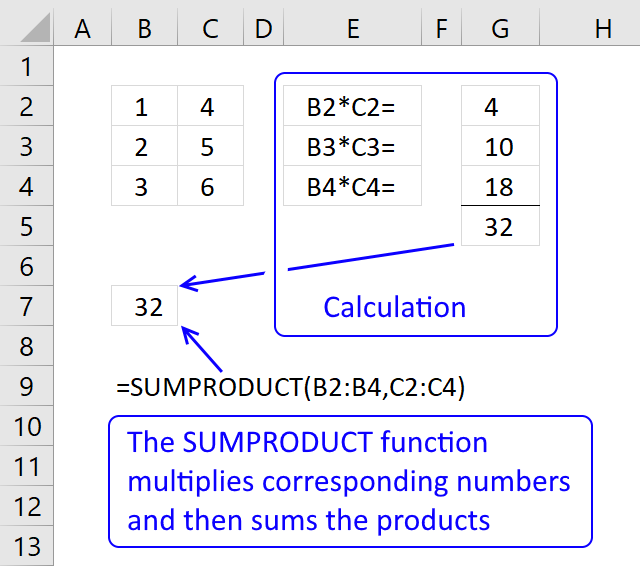
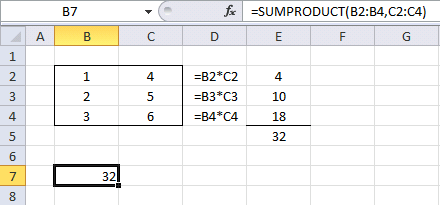
The SUMPRODUCT function calculates the product of corresponding values and then returns the sum of each multiplication.
SUMPRODUCT function example
The picture above shows how the SUMPRODUCT works in greater detail.
Formula in cell B7:
The SUMPRODUCT function multiplies cell ranges row by row and then adds the numbers and returns a total. The formula in cell B7 multiples values 1*4= 4, 2*5 = 10 and 3*6 =18 and then adds the numbers 4+10+18 equals 32.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Syntax
- Things to know a
- How to use
- How to use a logical expression
- How to use multiple conditions
- How to use OR logic
- Sum unique distinct invoices
- Count cells equal to any value in a list
- Count dates inside a date range
- Get Excel *.xlsx file
- Sum based on OR - AND logic
- Find empty cells and sum cells above
- Nested IF functions
- If not blank
- Returns nothing (blank)
- If not NA
- If not error
- Based on a list of values
- Multiple conditions and a date range
- Multiple date ranges
- Sum based on daily currency rates
- Get Excel *.xlsx file
- How to simplify IF functions
- If greater than 0 (zero)
- If between two dates
- If cell contains text
- If or
- Get Excel file
1. Introduction
What is product?
A product refers to the result obtained when two or more numbers (or factors) are multiplied together. The outcome of multiplying numbers together. For example, in the multiplication equation a × b = c, number c is called the product of a and b.
What is a sum?
The sum in mathematics refers to the result of adding two or more numbers or terms together. The sum can be expressed using summation notation, denoted by the Greek letter sigma (Σ). For example, 1+2+3+4+5 equals 15.
2. Syntax
SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
| array1 | Required. Required. The first array argument whose numbers you want to multiply and then sum. |
| [array2] | Optional. Up to 254 additional arguments. |
3. Things to know
The SUMPRODUCT function is one of the most powerful functions in Excel and is one that I often use. I highly recommend learning how it works.
The SUMPRODUCT function requires you to enter it as a regular formula, not an array formula. However, there are exceptions. If you use a logical expression you must enter the formula as an array formula and convert the boolean values to their equivalents.
There are workarounds to this problem which I will demonstrate in the examples below.
4. How to use
This example demonstrates how the SUMPRODUCT function works.
Formula in cell B7:
4.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Multiplying values on the same row
The first array is in cell range B2:B4 and the second array is in cell range C2:C4.
B2:B4*C2:C4
becomes
{1;2;3} * {4;5;6}
becomes
{1*4; 2*5; 3*6}
and returns {4; 10; 18}.
The same calculations are done in column D and shown in column E, see above picture.
Step 2 - Return the sum of those products
{4; 10; 18}
becomes
4 + 10 + 18
and the function returns 32 in cell B7.
The same calculation is done E5, the sum of the products in cell range E2:E4 is calculated in cell E5. See the above picture.
Now you know the basics. Let's move on to something more interesting.
5. How to use a logical expression
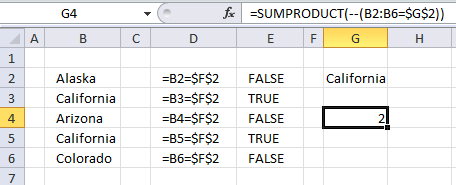
The image above demonstrates a formula in cell G4 that counts how many cells that is equal to the value in cell G2. Note, that this is only an example. I recommend you use the COUNTIF function to count cells based on a condition, it is designed to do that.
Formula in cell G4:
5.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Logical expression returns a boolean value that we must convert to numbers
There is only one array in this formula but something else is distorting the picture. A comparison operator (equal sign) and a second cell value (G2) or a comparison value. With these, we have now built a logical expression. This means that the value in cell G2 is compared to all the values in cell range B2:B6 (not case sensitive).
B2:B6=$G$2
becomes
{"Alaska";"California";"Arizona";"California";"Colorado"}="California"
and returns
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE}.
They are all boolean values and excel can´t sum these values. We have to convert the values to numerical values. There are a few options, you can:
- Add a zero - (B2:B6=$G$2)+0
- Multiply with 1 - (B2:B6=$G$2)*1
- Double negative signs --(B2:B6=$G$2)
They all convert boolean values to their numerical equivalents. TRUE is 1 and FALSE is 0 (zero).
--( {FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE})
becomes
{0;1;0;1;0}
Step 2 - Return the sum of those products
{0;1;0;1;0}
becomes
0 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0
and returns 2 in cell G4. There are two cells containing the value "California" in cell range B2:B6.
You accomplish the same thing using the COUNTIF function or count multiple values in different columns using the COUNTIFS function. In fact, you can count entire records in a data set using the COUNTIFS function.
6. How to use multiple conditions
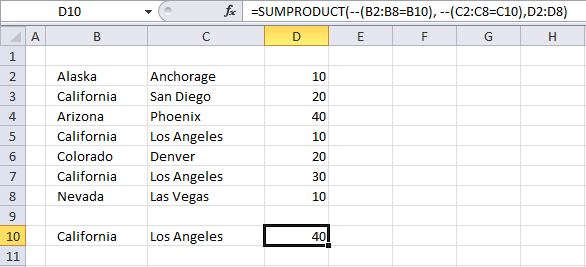
This example shows how to use multiple conditions in the SUMPRODUCT function using AND logic. AND logic means that all conditions must be met on a given row in order to add the number to the total.
Formula in cell D10:
This formula contains three arguments, the SUMPRODUCT function allows you to use up to 30 arguments. You can make the formula somewhat shorter:
This also allows you to have a lot more conditions than 30 if you like and use OR logic if you want. Example 4 demonstrates OR logic.
It is only the available computer memory that is the limit if you use this method. The formula looks like an array formula but no, you are not required to enter it as an array formula.
6.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Multiplying corresponding components in the given arrays
The first logical expression B2:B8=B10 uses an equal sign to check if the values in cell range B2:B8 are equal to the value in cell B10.
B2:B8=B10
becomes
{"Alaska";"California";"Arizona";"California";"Colorado";"California";"Nevada"}="California"
and returns
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE}.
The second logical expression is C2:C8=C10, the other logical operators you can use are:
- = equal
- < less than
- > greater than
- <> not equal to
- <= less than or equal to
- >= larger than or equal to
C2:C8=C10
becomes
{"Anchorage";"San Diego";"Phoenix";"Los Angeles";"Denver";"Los Angeles";"Las Vegas"}="Los Angeles"
and returns
{FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE}.
The third and last logical
(B2:B8=B10)*(C2:C8=C10)*D2:D8
becomes
({FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE})*({FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE})*{10; 20; 40; 10; 20; 30; 10}
becomes
{0;0;0;1;0;1;0}*{10; 20; 40; 10; 20; 30; 10}
and returns
{0; 0; 0; 10; 0; 30; 0}
Step 2 - Return the sum of those products
{0; 0; 0; 10; 0; 30; 0}
becomes
10 +30
and returns 40 in cell D10.
7. How to use OR logic
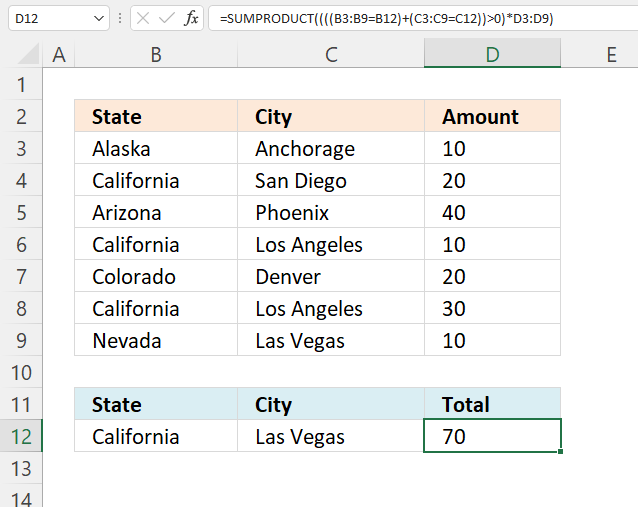
This example shows how to use multiple conditions. A number in cell range D3:D9 is added if the item in cell B12 is found on the corresponding row in cell range B3:B9 OR if the item in C12 is found in cell range C3:C9.
Formula in cell D10:
Explaining formula in cell D10
Step 1 - Compare values to condition
The equal sign lets you compare the condition to values in B3:B9, the result is an array with the same size as B3:B9 containing TRUE or FALSE.
B3:B9=B12
becomes
{"Alaska"; "California"; "Arizona"; "California"; "Colorado"; "California"; "Nevada"}="California"
and returns
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE}.
Step 2 - Compare values to condition
C3:C8=C12
becomes
{"Anchorage"; "San Diego"; "Phoenix"; "Los Angeles"; "Denver"; "Los Angeles"; "Las Vegas"}="Las Vegas"
and returns
{FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}.
Step 3 - Apply OR logic
We need to add numbers if at least one of the conditions matches on the same row, this means OR logic.
Mathematical operators between arrays allow you to do more complicated calculations, like this:
* (asterisk) - Both logical expressions must match (AND logic)
+ (plus sign) - Any of the logical expressions must match, it can be all it can be only one. It doesn't matter. (OR logic)
The AND logic behind this is that
- TRUE * TRUE = TRUE (1)
- TRUE * FALSE = FALSE (0)
- FALSE * FALSE = FALSE (0)
The OR logic works like this:
- TRUE + TRUE = TRUE (1)
- TRUE + FALSE = TRUE (1)
- FALSE + FALSE = FALSE (0)
The numbers above show the numerical equivalent of each result. True equals 1 and False equals 0 (zero).
The parentheses shown below let you control the order of calculation, we must do the comparisons before we add the arrays.
(B2:B8=B10)+(C2:C8=C10)
becomes
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE} + {FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}
and returns {0; 1; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1}.
Step 4 - Check if result is larger than 0 (zero)
If both values match the conditions the result is two, the result will be twice as much. We can't multiply with two, the larger than character checks if the result is larger than 0 (zero).
((B3:B9=B12)+(C3:C9=C12))>0
becomes
{0; 1; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1}>0
and returns {FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 5 - Multiply with numbers
((B2:B8=B10)+(C2:C8=C10))*D2:D8
becomes
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}*D2:D8
becomes
{FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}*{10; 20; 40; 10; 20; 30; 10}
and returns {0; 20; 0; 10; 0; 30; 10}.
Step 6 - Add numbers and return total
SUMPRODUCT(((B2:B8=B10)+(C2:C8=C10))*D2:D8)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0; 20; 0; 10; 0; 30; 10})
and returns 70.
These expressions check if California is found in cell range B2:B8 or Las Vegas is found in cell range C2:C8. They are found in rows 4, 6,8, and 9.
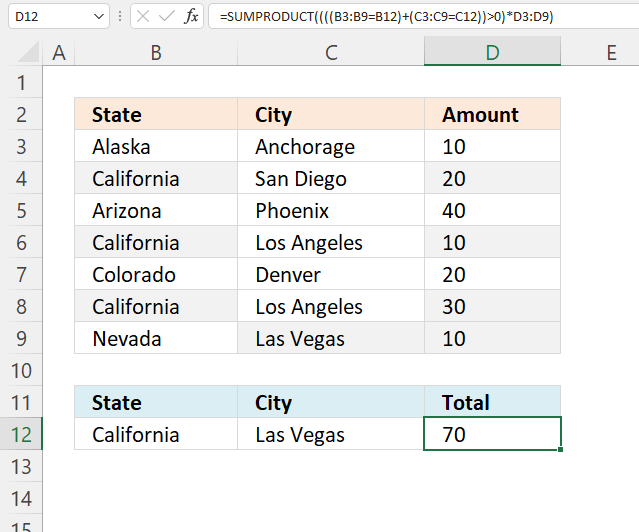
The SUMPRODUCT function sums the corresponding values in column D and returns 70 in cell D10. 20+10+30+10 equals 70.
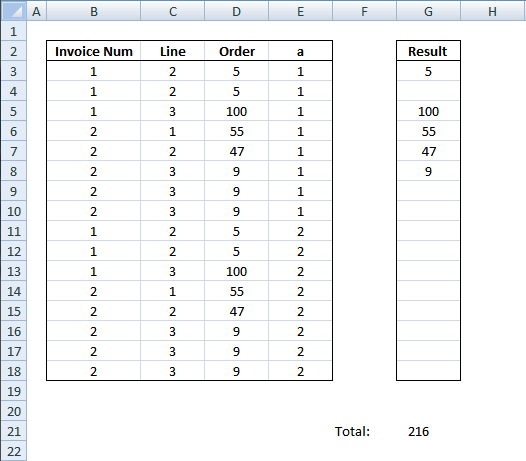
8. Sum unique distinct invoices
Question:
I have a long table The key is actually col B&C BUT…sometime there are few rows with same key (like rows 3:4 or rows 8:10). I'd like to sum data in column D and to consider same key rows as one row.
Desired result 216
Can I also add condition that Column E=1 ?
Answer:
I highly recommend a pivot table for this task, it is extremely fast which is good if you have lots of data to work with. This article demonstrates a formula that returns a total based on a condition.
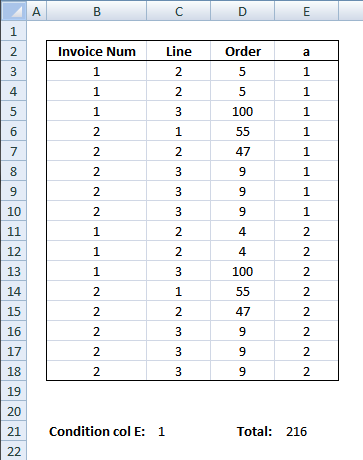
Formula in cell E21:
This formula removes duplicate records and sums values in col D.
Explaining the formula in cell E21
To simplify the explanation I am replacing cell references with named ranges. The formula becomes:
Named Ranges
ColB - $B$3:$B$18
ColC - $C$3:$C$18
ColD - $D$3:$D$18
ColE - $E$3:$E$18
Step 1 - Filter records equal to condition in cell E21
The equal sign lets you compare the values in column E with the condition in cell C21, this is a logical expression and the result is either TRUE or FALSE (boolean values), however, the SUMPRODUCT function can't work with boolean values. We need to convert the TRUE and FALSe to their numerical equivalents. TRUE = 1 and FALSE = 0 (zero).
--(ColE=$C$21)
--({1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2; 2}=1)
becomes
--({TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE})
Sumproduct can´t calculate TRUE/FALSE values. Let´s convert values to 1 and 0.
--({TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE})
becomes
{1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0}
Step 2 - Create an array with values from col D
ColD
becomes
{5; 5; 100; 55; 47; 9; 9; 9; 4; 4; 100; 55; 47; 9; 9; 9}
Step 3 - Count duplicate records
The COUNTIFS function calculates the number of cells across multiple ranges that equals all given conditions.
1/COUNTIFS(ColB, ColB, ColC, ColC, ColD, ColD, ColE, ColE)
becomes
1/{2; 2; 1; 1; 1; 3; 3; 3; 2; 2; 1; 1; 1; 3; 3; 3}
and returns
{0,5; 0,5; 1; 1; 1; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,5; 0,5; 1; 1; 1; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333}
Step 4 - Return the sum of the products of the corresponding arrays
=SUMPRODUCT(--(ColE=$C$21), ColD, 1/COUNTIFS(ColB, ColB, ColC, ColC, ColD, ColD, ColE, ColE))
becomes
=SUMPRODUCT({1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0}, {5; 5; 100; 55; 47; 9; 9; 9; 4; 4; 100; 55; 47; 9; 9; 9}, {0,5; 0,5; 1; 1; 1; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,5; 0,5; 1; 1; 1; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333; 0,333333333333333})
returns 216 in cell E21.
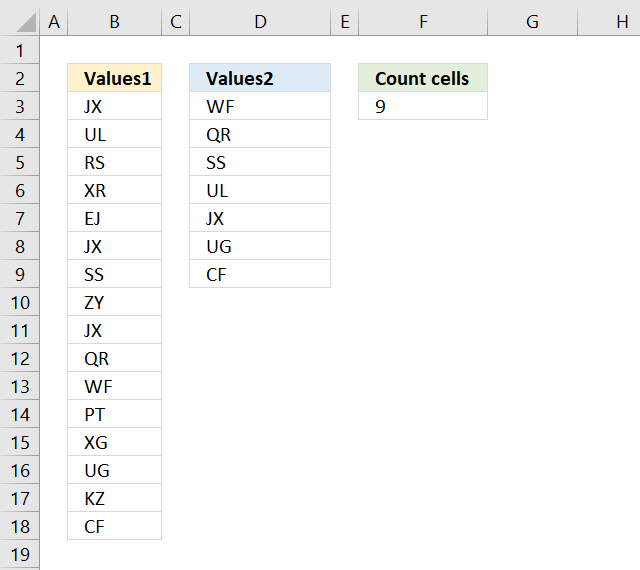
9. Count cells equal to any value in a list
The formula in cell F9 counts the number of cells in column B (Values1) that are equal to any of the values in column D (Values2).
Formula in cell F9:
Explaining formula in cell F9
The COUNTIF function allows you to count cells in a range that are equal to a criterion. The great thing about the COUNTIF function is that it is possible to use criteria.
COUNTIF(B3:B18,D3:D9)
becomes
COUNTIF({"JX"; "UL"; "RS"; "XR"; "EJ"; "JX"; "SS"; "ZY"; "JX"; "QR"; "WF"; "PT"; "XG"; "UG"; "KZ"; "CF"}, {"WF"; "QR"; "SS"; "UL"; "JX"; "UG"; "CF"})
and returns the following array: {1; 1; 1; 1; 3; 1; 1}
The SUMPRODUCT function lets you sum the values in the array without the need to enter the fomula as an array formula.
SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(B3:B18,D3:D9))
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({1; 1; 1; 1; 3; 1; 1})
and returns 9 in cell F9. 1+1+1+1+3+1+1 = 9
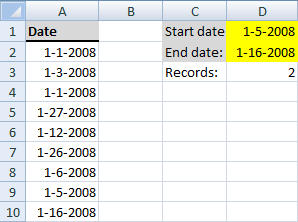
10. Count dates inside a date range
How do I automatically count dates in a specific date range?
Array formula in cell D3:
This is an array formula so make sure you press Ctrl + Shift + Enter.
Alternative array formula in cell D3:
If you want to count the start date and end date also, try this formula:
Alternative formula:
Explaining alternative formula in cell D3
=SUMPRODUCT(--($A$2:$A$10<=$D$2),--($A$2:$A$10>=$D$1))
Step 1 - Create a boolean array with matching dates to the first criterion
=SUMPRODUCT(--($A$2:$A$10<=$D$2),--($A$2:$A$10>=$D$1))
--($A$2:$A$10<=$D$2)
becomes
--({39448;39450;39448;39474;39459;39473;39453;39452;39463}<=39463)
becomes
--({39448;39450;39448;39474;39459;39473;39453;39452;39463}<=39463)
becomes
--({TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE})
becomes
{1;1;1;0;1;0;1;1;1}
Step 2 - Create a boolean array with matching dates to the second criterion
=SUMPRODUCT(--($A$2:$A$10<=$D$2),--($A$2:$A$10>=$D$1))
--($A$2:$A$10>=$D$1)
becomes
--({39448;39450;39448;39474;39459;39473;39453;39452;39463}>=39452)
becomes
--({FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE})
becomes
{0;0;0;1;1;1;1;1;1}
Step 3 - All together
=SUMPRODUCT(--($A$2:$A$10<=$D$2),--($A$2:$A$10>=$D$1))
becomes
=SUMPRODUCT({1;1;1;0;1;0;1;1;1},{0;0;0;1;1;1;1;1;1})
becomes
=SUMPRODUCT({0;0;0;0;1;0;1;1;1}) returns 4.
Get Excel *.xls
count-records-between-two-dates-in-excel.xls
Get Excel *.xlsx file
Count cells equal to a value in a list.xlsx
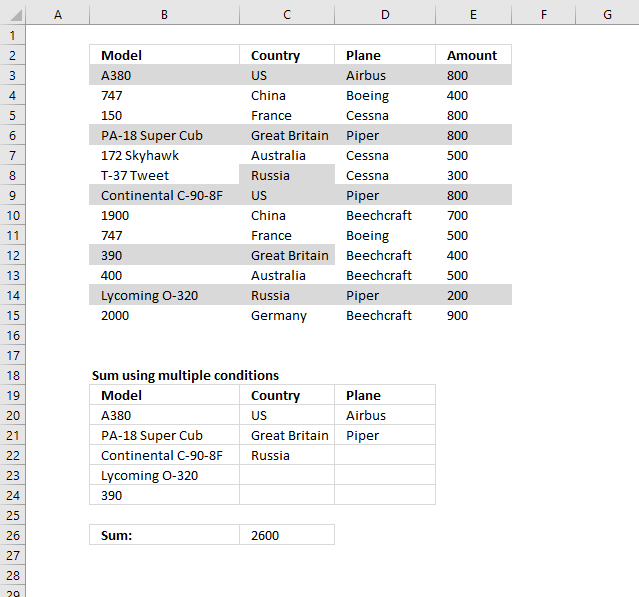
12. Sum based on OR - AND logic
Question:
It's easy to sum a list by multiple criteria, you just use array formula a la: =SUM((column_plane=TRUE)*(column_countries="USA")*(column_producer="Boeing")*(column_to_sum))
But all these are single conditions -- you can't pass multiple conditions, say for example: USA or China or France in column_countries and Airbus or Boeing in column_producer. I know 2 solutions to get around this limitation, but none is perfect:
1) =SUM((column_plane=TRUE)*((column_countries="USA")+(column_countries="China")+(column_countries="France"))* ((column_producer="Airbus") + (column_producer="Boeing"))*(column_to_sum)) -- this one works great, but it's not dinamic at all. What if the user chooses 10 multiple countries or more? You're not gonna write tens of equations for each condition.
2) =SUM((column_countries= IF(TRANSPOSE(contries_selected)=TRUE, TRANSPOSE(countries_selected_names)))*(column_producer="Airbus")*(column_to_sum)) -- that works fine, but this is producing a 2-dimentional matrix and hence is good for one condition only -- notice column_producer has only one value. Now, what if you want to pass multiple values to column_producer as well?
In SQL this equates to
SELECT SUM(column_to_sum)
FROM table
WHERE
(country = "USA" OR country = "France" OR country = "China")
AND
(producer ="Boeing" OR producer="Airbus")
Any idea how to replicate that in Excel???
You can find the question here.
Answer:
The criteria is in B20:D25, I have colored the cells that match. Here is how to avoid writing ten's of equations:
Formula in C26:
Explaining formula in cell C26
Step 1 - Identify criteria B20:B25 in B3:B15
The COUNTIF function counts values based on a condition or criteria. If a match is found 1 is returned and if not found then it returns 0 (zero).
COUNTIF(B20:B25, B3:B15)
becomes
COUNTIF({"A380"; "PA-18 Super Cub"; "Continental C-90-8F"; "Lycoming O-320"; 390; 0},{"A380"; 747; 150; "PA-18 Super Cub"; "172 Skyhawk"; "T-37 Tweet"; "Continental C-90-8F"; 1900; 747; 390; 400; "Lycoming O-320"; 2000})
and returns
{1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 0}
Step 2 - Identify criteria C20:C25 in C3:C15
COUNTIF(C20:C25, C3:C15)
becomes
COUNTIF({"US"; "Great Britain"; "Russia"; 0; 0; 0},{"US"; "China"; "France"; "Great Britain"; "Australia"; "Russia"; "US"; "China"; "France"; "Great Britain"; "Australia"; "Russia"; "Germany"})
and returns
{1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 0}
Step 3 - Identify criteria D20:D25 in D3:D15
COUNTIF(D20:D25,D3:D15)
becomes
COUNTIF({"Airbus"; "Piper"; 0; 0; 0; 0},{"Airbus"; "Boeing"; "Cessna"; "Piper"; "Cessna"; "Cessna"; "Piper"; "Beechcraft"; "Boeing"; "Beechcraft"; "Beechcraft"; "Piper"; "Beechcraft"})
and returns
{1;0;0;1;0;0;1;0;0;0;0;1;0}
Step 4 - Multiply arrays
All conditions must be TRUE in order to return TRUE.
COUNTIF(B20:B25,B3:B15)*COUNTIF(C20:C25,C3:C15)*COUNTIF(D20:D25,D3:D15)
becomes
{1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 0}*{1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 1; 0}*{1;0;0;1;0;0;1;0;0;0;0;1;0}
and returns
{1;0;0;1;0;0;1;0;0;0;0;1;0}
Step 5 - Multiply array with amounts
COUNTIF(B20:B25, B3:B15)*COUNTIF(C20:C25, C3:C15)*COUNTIF(D20:D25, D3:D15)*E3:E15
becomes
{1;0;0;1;0;0;1;0;0;0;0;1;0}*E3:E15
becomes
{1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 1; 0; 0; 0; 0; 1; 0}*{800; 400; 800; 800; 500; 300; 800; 700; 500; 400; 500; 200; 900}
and returns
{800;0;0;800;0;0;800;0;0;0;0;200;0}
Step 6 - Sum array
The SUMPRODUCT function then adds the numbers and returns a total.
SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(B20:B25, B3:B15)*COUNTIF(C20:C25, C3:C15)*COUNTIF(D20:D25, D3:D15)*E3:E15)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({800;0;0;800;0;0;800;0;0;0;0;200;0})
and returns 2600. 800 + 800 + 800 + 200 = 2600.
Get Excel *.xlsx file
pass multiple conditions dynamically.xlsx
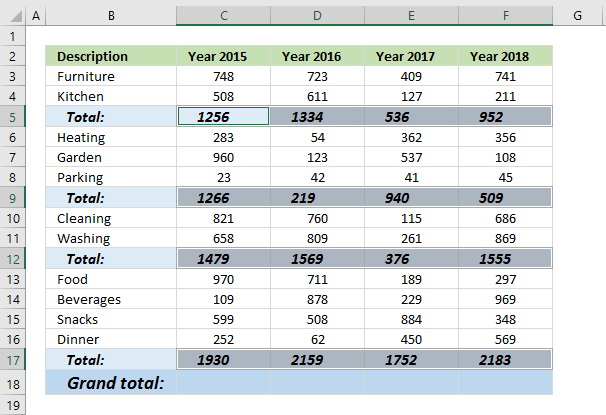
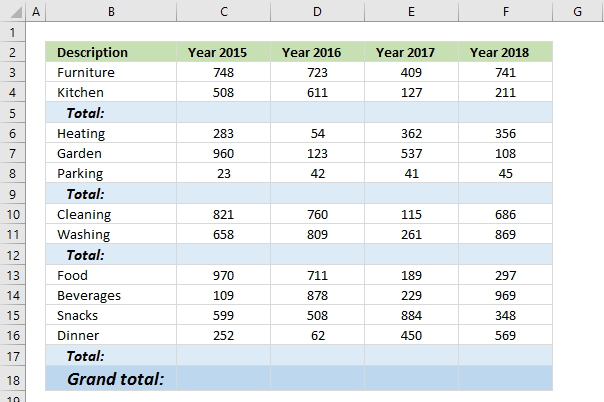
13. Find empty cells and sum cells above
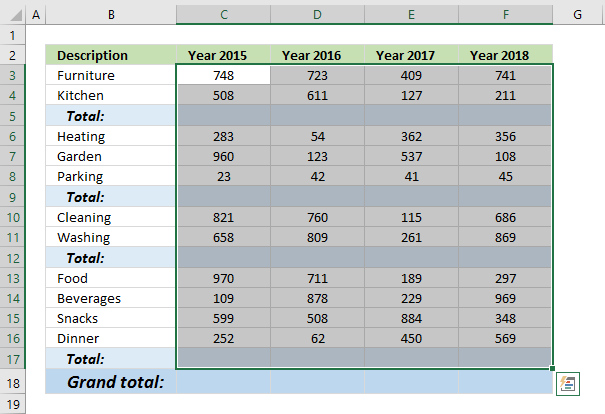
This article demonstrates how to find empty cells and populate them automatically with a formula that adds numbers above and returns a total.
Is it possible to quickly select all empty cells and then sum cells above to the next empty cell? Yes, I will show you how.
Can I have a formula in grand total (row 18) that only sums all the totals above? Yes!
13.1. How to select empty cells in a cell range
The image above demonstrates how to find empty cells in a given cell range.
- Select all values and the blank total cells.
- Press F5, a dialog box appears.
- Press the left mouse on the "Special..." button.
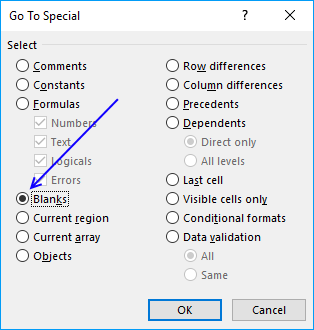
- Press on "Blanks" to select it, then press on the "OK" button.
13.2. Populate empty cells with a formula
- Go to tab "Home" on the ribbon and press with left mouse button on the "AutoSum" button.
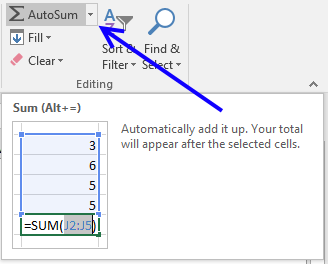
- All empty cells now have a SUM formula that adds all the above values to the next SUM formula.
13.3. Add grand totals that only sums cells populated with formulas
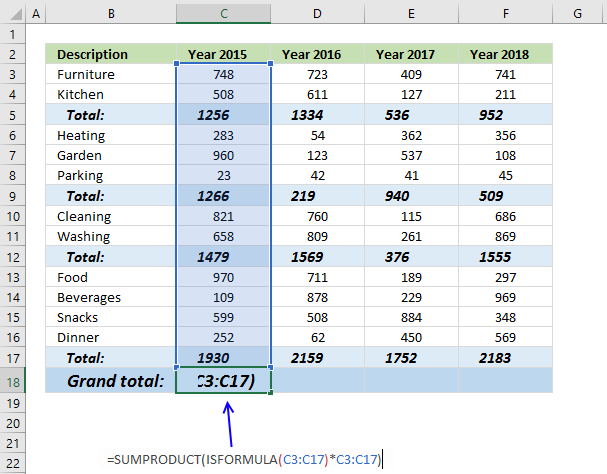
- Select cell C18 and type this formula:
=SUMPRODUCT(ISFORMULA(C3:C17)*C3:C17)
- Press Enter. Copy cell C18 and paste to cell range D18:F18.
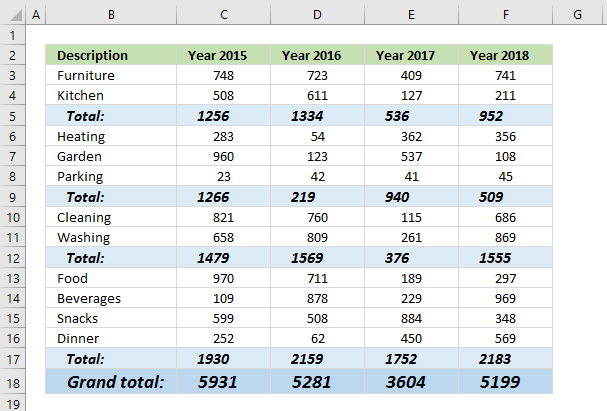
13.3.1 Explaining formula in cell C18
Step 1 - Check if cell contains a formula
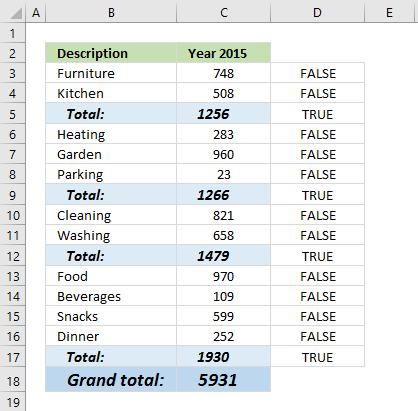
The ISFORMULA function checks if a cell in cell range C3:C17 has a formula. It returns TRUE or FALSE.
ISFORMULA(C3:C17)
returns this array:
{FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}
The picture below shows this array in column D.
The array shows that there is a formula in C5, C9, C12, and C17.
Step 2 - Multiply with value
The asterisk character allows you to multiply numbers and boolean values.
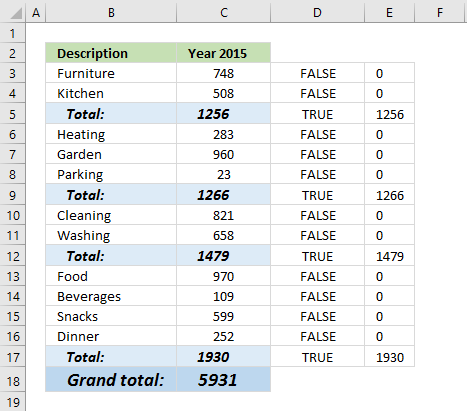
ISFORMULA(C3:C17)*C3:C17 multiplies the boolean values with their corresponding values in column C, shown in column E below.
ISFORMULA(C3:C17)*C3:C17
becomes
{FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}*C3:C17
becomes
{FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}*{748; 508; 1256; 283; 960; 23; 1266; 821; 658; 1479; 970; 109; 599; 252; 1930}
and returns
{0; 0; 1256; 0; 0; 0; 1266; 0; 0; 1479; 0; 0; 0; 0; 1930}
Step 3 - Add values and return the total
The SUMPRODUCT function then sums all values in the array.
SUMPRODUCT(ISFORMULA(C3:C17)*C3:C17)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0; 0; 1256; 0; 0; 0; 1266; 0; 0; 1479; 0; 0; 0; 0; 1930})
and returns 5931 in cell C18.
Why not use the SUM function? You need to enter it as an array formula if you use the SUM function. Use the SUM function if you are an Excel 365 user.
13.4. Add grand totals that only sums cells populated with formulas - Excel 2013
The following formula won't work, the SUMIF function seems to not be capable of processing the ISFORMULA function. The ISFORMULA function is an Excel 2013 function, they seem incompatible.
=SUMIF(C3:C17, ISFORMULA(C3:C17))
Let me know if you have a solution that allows me to use the SUMIF function.
13.5. Add grand totals that only sums cells populated with formulas - Excel 365
=SUM(FILTER(C3:C17, ISFORMULA(C3:C17)))
5.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Check if cell contains formula
The ISFORMULA function returns a boolean value TRUE or FALSE if a cell contains a formula or not.
ISFORMULA(C3:C17)
Step 2 - Filter numbers based on boolean values
FILTER(C3:C17,ISFORMULA(C3:C17))
Step 3 - Add numbers and return a total
SUM(FILTER(C3:C17,ISFORMULA(C3:C17)))
Recommended articles
- SUMPRODUCT function (Microsoft Excel)
- SUMPRODUCT function (Xelplus)
- SUMPRODUCT Function (ExcelJet)
14. Nested IF functions
I have demonstrated in a previous post how to simplify nested IF functions, in this section I will show you how to simplify your SUMPRODUCT formulas regarding multiple criteria.
Table of Contents
- SUMPRODUCT - nested IF functions
- SUMPRODUCT - weighted average based on percentages
- SUMPRODUCT - weighted average
- Get Excel *.xlsx file
14.1. SUMPRODUCT - nested IF functions
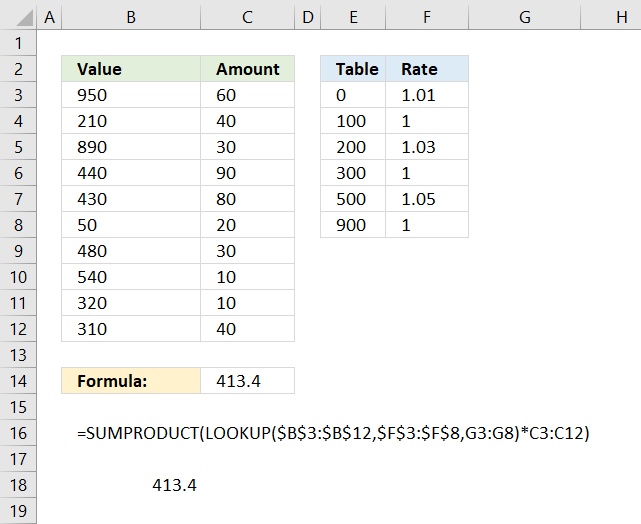
The formula in cell C14 multiplies numbers with a rate based on the size of the number and returns a total. The table in E2:F8 shows the different rates and the corresponding criteria.
For example, numbers between 0 (zero) and 100 have a rate multiplier of 1.01. Numbers between 100 and 200 are multiplied by 1.
Formula in cell C14:
14.1.1 Explaining formula
In most cases, there is no need for IF functions in SUMPRODUCT formulas, this is true in this case as well, the criteria below are complicated to build with IF functions.
0 <= value < 100 Rate: 1.01
100 <= value < 200 Rate: 1
200 <= value < 300 Rate: 1.03
300 <= value < 500 Rate: 1
500 <= value < 900 Rate: 1.05
900 <= value Rate: 1
Step 1 - Map numbers to corresponding rates
If a value in column B is matching one of the above ranges the corresponding rate is used.
However, it can be easily simplified using the LOOKUP function. The following formula is entered in cell C14 in the image above.
A small table is easy to build, shown in columns E and F. The LOOKUP function requires the values in E3:E8 to be sorted in ascending order for it to work properly.
Instead of using one lookup value in the first argument, I am using an entire cell range.
LOOKUP(B3:B12,E3:E8,F3:F8)
The rate is determined by the value in B3:B12.
LOOKUP({950; 210; 890; 440; 430; 50; 480; 540; 320; 310},{0; 100; 200; 300; 500; 900},{1.01; 1; 1.03; 1; 1.05; 1})
The LOOKUP function matches the values in B3:B12 to the values in F3:F8 and returns the corresponding value from G3:G8 simultaneously.
{1; 1.03; 1.05; 1; 1; 1.01; 1; 1.05; 1; 1}
Step 2 - Multiply numbers with rates
Now we know which rates to use, it is now possible to multiply the amounts.
LOOKUP($B$3:$B$12,$E$3:$E$8,F3:F8)*C3:C12
becomes
{1; 1.03; 1.05; 1; 1; 1.01; 1; 1.05; 1; 1}*C3:C12
becomes
{1; 1.03; 1.05; 1; 1; 1.01; 1; 1.05; 1; 1}*{60; 40; 30; 90; 80; 20; 30; 10; 10; 40}
and returns
{60; 41.2; 31.5; 90; 80; 20.2; 30; 10.5; 10;40}.
Step 3 - Add results and return a total
Lastly, the SUMPRODUCT function adds all numbers and returns a total.
SUMPRODUCT({60; 41.2; 31.5; 90; 80; 20.2; 30; 10.5; 10; 40})
and returns 413.4 in cell C14.
Equivalent formula using nested IF functions
So what would the equivalent formula look like using IF functions?
Verify that the formula works
Column D is a column to verify the calculation, you don't need it.
14.2. Weighted average based on percentages
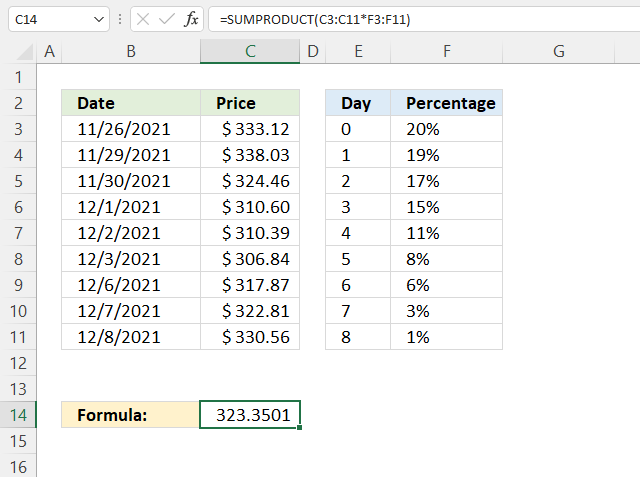
The image above demonstrates a formula that calculates the weighted average for a given date using percentages. This technique can be used to create a weighted moving average often used in stock charts.
The weighted moving average puts more weight towards recent dates making the weighted moving average follow price more closely than the simple moving average. The image above, however, puts more weight on earlier dates.
Formula in cell C14:
The percentages are specified in F3:F11 and the total must be 1. 0.2 + +.19 + 0.17 + 0.15 + 0.11 + 0.08 + 0.06 + 0.03 + 0.01 equals 1.
To create a moving weighted average lock the reference pointing to the percentages by converting it to an absolute cell reference.
You can now copy cell C14 and paste it to cells below to calculate a running weighted average or weighted moving average. You need to have more price data than I have shown in the image above to make it work.
Explaining formula in cell C14
Step 1 - Multiply price data with percentages
The asterisk lets you multiply value with value, this works fine with cell ranges as well.
C3:C11*$F$3:$F$11
becomes
{333.12; 338.03; 324.46; 310.6; 310.39; 306.84; 317.87; 322.81; 330.56}*{0.2; 0.19; 0.17; 0.15; 0.11; 0.08; 0.06; 0.03; 0.01}
and returns
{66.624; 64.2257; 55.1582; 46.59; 34.1429; 24.5472; 19.0722; 9.6843; 3.3056}.
Step 2 - Add results and return a total
SUMPRODUCT(C3:C11*F3:F11)
becomes
{66.624; 64.2257; 55.1582; 46.59; 34.1429; 24.5472; 19.0722; 9.6843; 3.3056}
and returns 323.3501 in cell C14.
14.3. Weighted average
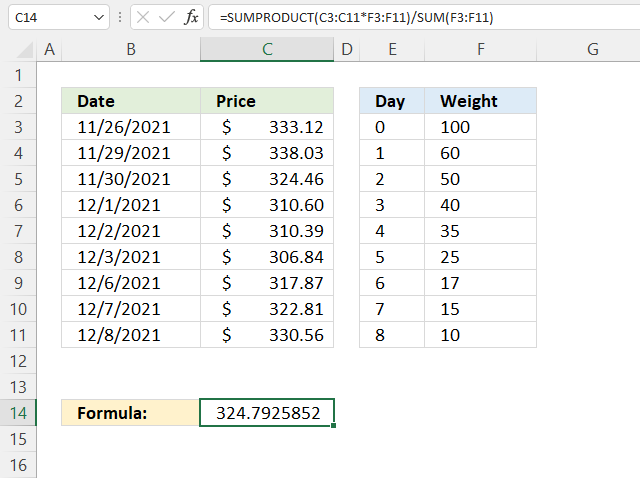
The example demonstrates how to use weights to create a weighted average, there is no requirement that the sum is 100 or 1 the formula takes care of that.
Formula in cell C14:
Explaining formula in cell C14
Step 1 - Multiply price data with weights
The asterisk lets you multiply value with value in Excel, this works fine with cell ranges as well.
C3:C11*F3:F11
becomes
{333.12; 338.03; 324.46; 310.6; 310.39; 306.84; 317.87; 322.81; 330.56}*{100; 60; 50; 40; 35; 25; 17; 15; 10}
and returns
{33312; 20281.8; 16223; 12424; 10863.65; 7671; 5403.79; 4842.15; 3305.6}.
Step 2 - Add results and return a total
SUMPRODUCT(C3:C11*F3:F11)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({33312; 20281.8; 16223; 12424; 10863.65; 7671; 5403.79; 4842.15; 3305.6})
and returns 114326.99.
Step 3 - Divide by sum
The SUM function adds numbers from a cell range and returns a total.
SUMPRODUCT(C3:C11*F3:F11)/SUM(F3:F11)
becomes
114326.99/SUM(F3:F11)
becomes
114326.99/352
and returns 324.792585227273.
14.4 Get Excel *.xlsx file
15. If not blank
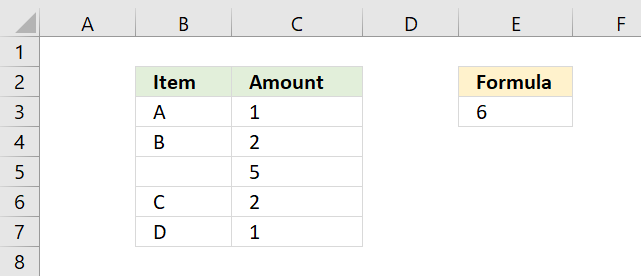
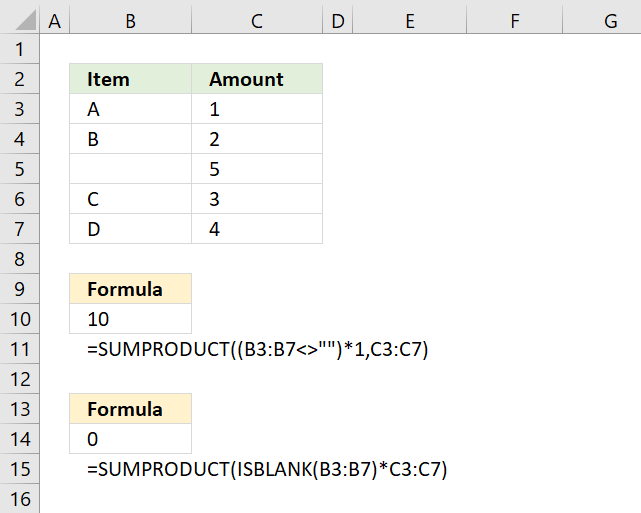
The above image demonstrates how to ignore blank cells in a SUMPRODUCT formula. The following formula is shown in cell E3.
It adds numbers and returns a total if the corresponding value in B3:B7 is not a blank cell. For example, cells B3, B4, B6, and B7 have values and the corresponding cells in C3:C7 are C3, C4, C6, and C7. The total is 1 + 2 + 2 + 1 equals 6.
There is no need for an IF function, simply use the ISBLANK function and then multiply with the corresponding cell range.
15.1 Explaining formula in cell E3
Step 1 - Identify blank cells
The ISBLANK function returns TRUE or FALSE based on if a cell is blank or not. Since we are using a cell range the ISBLANK function returns an array with the same size as the cell range.
ISBLANK(value)
ISBLANK(B3:B7) returns {FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE}
Step 2 - Convert boolean to their opposites
The NOT function comes in handy when you want to convert the boolean values to their opposites. For example, TRUE becomes FALSE and FALSE becomes TRUE.
NOT(ISBLANK(B3:B7)) returns {TRUE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE}.
Step 3 - Multiply with numbers
The next step is to multiply the boolean array with cell range C3:C7. We can do that by using the asterisk character.
TRUE * number = number
FALSE * number = 0 (zero)
NOT(ISBLANK(B3:B7))*C3:C7 returns {1; 2; 0; 2; 1}.
Step 4 - Add numbers and return total
The SUMPRODUCT function then adds all numerical values in the array returning 6 in cell E3.
SUMPRODUCT(NOT(ISBLANK(B3:B7))*C3:C7)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({1; 2; 0; 2; 1})
and returns 6. 1+2+0+2+1 = 6
16. Returns nothing (blank)
Cell range B3:B7 contains a formula that sometimes returns a character and sometimes a blank. The ISBLANK function won't work in this case, see cell B14, it returns 0 which is incorrect.
We need to rely on the larger than and smaller than characters <>, see the formula in cell B10.
Together like this <> means not equal to. Two double quotes "" is nothing.
Step 1 - Identify cells returning nothing
B3:B7<>"" is a logical expression and returns an array of boolean values with as many values as the number of cells in the cell range B3:B7.
returns {TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 2 - Multiply with numbers
The parentheses determine the order of calculations, we need it to compare the cell range with nothing before multiplying with cell range C3:C7.
(B3:B7<>"")*C3:C7 returns {1; 2; 0; 3; 4}.
Step 3 - Add numbers and return a total
The SUMPRODUCT function sums all values in the array.
SUMPRODUCT({1; 2; 0; 3; 4}) returns 10 in cell B10. 1 + 2 + 0 + 3 + 4 = 10.
17. If not NA
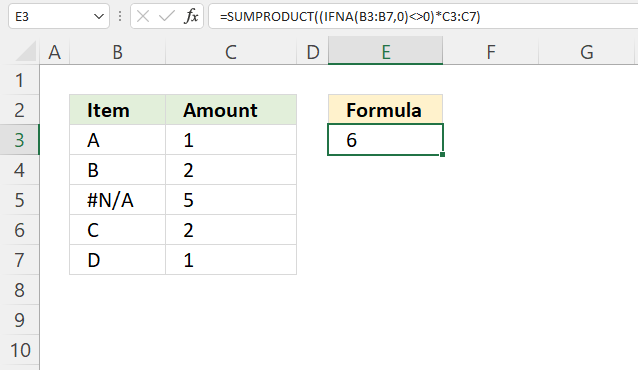
The formula in cell E6 adds numbers from C3:C7 if the corresponding values on the same row in B3:B7 are not a N/A# error and returns a total.
Formula in cell E3:
Explaining formula in cell E3
Step 1 - Identify NA errors
The IFNA function handles #N/A errors only, it returns a specific value if the formula or cell returns a #N/A error.
IFNA(value, value_if_na)
IFNA(B3:B7, 0) returns {"A"; "B"; 0; "C"; "D"}.
Notice how the N/A error value returns a 0 (zero).
Step 2 - Check if value is 0 (zero)
The less than and the greater than character combined evaluates to "not equal to", the result is a boolean value TRUE or FALSE.
IFNA(B3:B7, 0)<>0 returns {TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 3 - Multiply with numbers
The parentheses let you control the order of operation, the asterisk multiples the array with the numbers in C3:C7.
(IFNA(B3:B7, 0)<>0)*C3:C7 returns {1; 2; 0; 2; 1}.
Step 4 - Add numbers and return total
SUMPRODUCT((IFNA(B3:B7, 0)<>0)*C3:C7) returns 6 in cell E3. 1 + 2 + 0 + 2 + 1 equals 6.
18. If not error
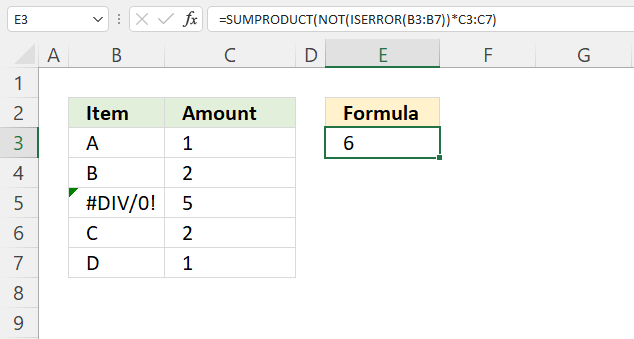
This formula ignores all error values and adds only numbers where the corresponding value on the same row is not an error.
Formula in cell E3:
For example, cell range B3:B7 contains values except for cell B5. It contains an error value, the formula adds numbers from cells C3, C4, C6, and C7 but not cell C5.
Explaining formula in cell E3
Step 1 - Identify errors
The ISERROR function returns a boolean value TRUE or FALSE if the value is an error value.
ISERROR(value)
ISERROR(B3:B7) returns {FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE}.
Step 2 - Convert boolean value to their opposites
The NOT function converts boolean values to their opposites. For example, TRUE becomes FALSE and FALSE becomes TRUE.
NOT(value)
NOT(ISERROR(B3:B7)) returns {TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 3 - Multiply with numbers
The parentheses let you control the order of operation, the asterisk multiples the array with the numbers in C3:C7.
NOT(ISERROR(B3:B7))*C3:C7
becomes
{TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}*C3:C7 returns {1; 2; 0; 2; 1}
Step 4 - Add numbers and return total
SUMPRODUCT(NOT(ISERROR(B3:B7))*C3:C7) returns 6. 1 + 2 + 0 + 2 + 1 equals 6.
Get Excel *.xlsx file
19. Based on a list of values
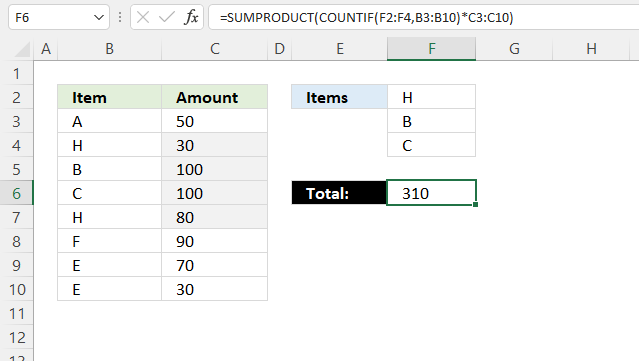
The image above shows how to sum numbers in column C based on a list of conditions specified in cell range F2:F3.
If the cells in cell range B3:B10 equals any of the conditions the corresponding amount in column C is added to the total.
Check out this article if you want to apply conditions to a column each: How to use multiple conditions in the SUMPRODUCT function
Formula in cell F6:
19.1 Explaining formula in cell F6
Step 1 - Identify matching items
The COUNTIF function calculates the number of cells that is equal to a condition. You can also use the COUNTIF function to count cells based on multiple conditions, the result is an array containing numbers that correspond to the cell range.
COUNTIF(range, criteria)
COUNTIF(F2:F4, B3:B10)
becomes
COUNTIF({"H"; "B"; "C"},{"A"; "H"; "B"; "C"; "H"; "F"; "E"; "E"})
and returns
{0; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0; 0}. Notice that the array correspond to cell range B3:B10, values in cells F2:F4 are 1 in the array and cells not matching are 0 (zero).
Step 2 - Multiply array with numbers
The asterisk character lets you multiply values in Excel, it works fine with arrays as well.
COUNTIF(F2:F4, B3:B10)*C3:C10
becomes
{0; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0; 0}*C3:C10
becomes
{0; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0; 0}*{50; 30; 100; 100; 80; 90; 70; 30}
and returns
{0; 30; 100; 100; 80; 0; 0; 0}.
Step 3 - Add numbers and return a total
The SUMPRODUCT function calculates the product of corresponding values and then returns the sum of each multiplication.
SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(F2:F4, B3:B10)*C3:C10)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0; 30; 100; 100; 80; 0; 0; 0})
and returns 310 in cell F6.
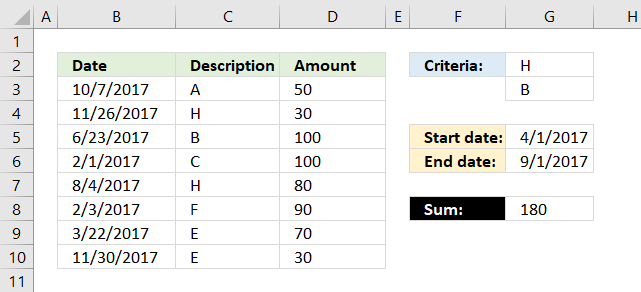
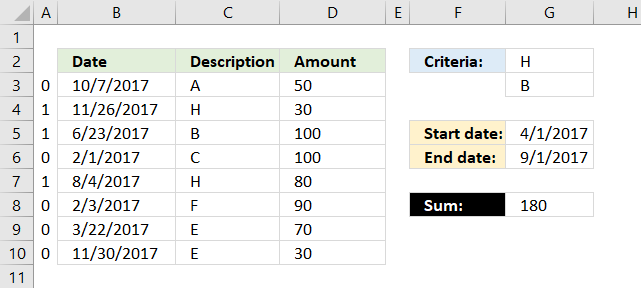
20. Multiple criteria
The formula above in cell G8 uses two conditions in cell G2 and G3 and a date range G5:G6 to create a total. The conditions in cell G2 and G3 are matched to the "Description" values in column C and the date range specified in cell G5 and G6 are used to filter values based on the dates in column B.
20.1 Explaining formula in cell G8
Step 1 - Identify values matching cell G2 and G3
The COUNTIF function allows you to compare multiple values to one column.
COUNTIF(G2:G3, C3:C10)
becomes
COUNTIF({"H";"B"},{"A";"H";"B";"C";"H";"F";"E";"E"})
and returns
{0;1;1;0;1;0;0;0}.
This tells us that the second, third and fifth value in column C matches G2 or G3.
The picture below shows the array in column A.
Step 2 - Identify values matching the date range
To match a date range we need two logical expressions, the first one checks if any of the dates in B3:B10 are larger than or equal to the start date in G5.
(G5<=B3:B10)
returns
{TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}.
The second logical expression matches dates smaller than or equal to the end date.
(G6>=B3:B10)
returns
{FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE}
Step 3 - Apply AND logic to all arrays
Column D shows the result of multiplying all arrays from the logical expressions and the COUNTIF function. This is the same as AND logic for values row-wise.
For example, the first value on row 3 is 0 (zero), the next is TRUE and the last value is FALSE. 0*TRUE*FALSE equals FALSE. All values must be TRUE to return TRUE.
Note, 0 (zero) is the same as FALSE and 1 is TRUE in Excel. Row 5 and 7 in column D return 1.
Step 4 - Sum all numbers in the array
The SUMPRODUCT function creates a total based on logical expressions.
SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(G2:G3,C3:C10)* (G5<=B3:B10)* (G6>=B3:B10)* D3:D10)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0;0;1;0;1;0;0;0}* D3:D10)
Lastly, multiply the array with the amounts in column D.
SUMPRODUCT({0;0;1;0;1;0;0;0}* {50; 30; 100; 100; 80; 90; 70; 30})
calculates to
SUMPRODUCT({0;0;100;0;80;0;0;0})
and returns 180 in cell G8.
21. Multiple date ranges
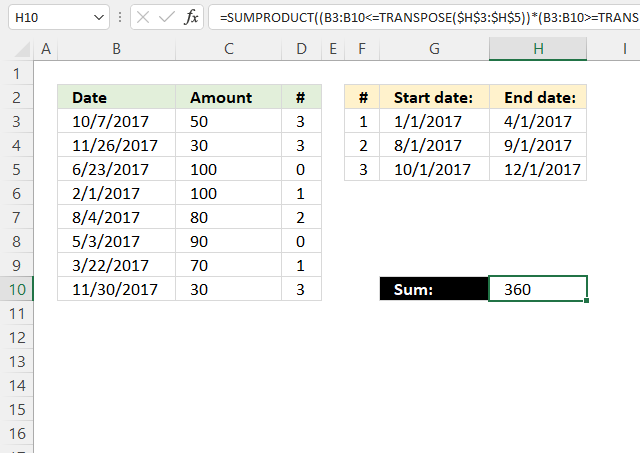
The following formula adds numbers based on date ranges, if the corresponding Excel date matches a date range the number is added to the total.
For example, cell B3 contains the date 10/7/2017 which matches the third date range. 10/7/2017 is earlier than or equal to 12/1/2017 and later than or equal to 10/1/2017.
The formula in cell H10 does this comparison to all dates in B3:B10 against the date ranges specified in G3:H5 and if they match the corresponding number in D3:D10 is added to a total.
Cell range D3:D10 contains which date range the date matches, cell D3 contains 3 and the corresponding date in B3 matches date range 3 10/1/2017 - 12/1/2017.
Formula in cell H10:
21.1 Explaining formula in cell H10
Step 1 - Transpose values
The TRANSPOSE function rearranges values from horizontal to vertical or vice versa.
TRANSPOSE(array)
TRANSPOSE(H3:H5)
becomes
TRANSPOSE({42826; 42979; 43070})
and returns {42826, 42979, 43070}.
Notice how the delimiting characters change, the semicolon is converted to a comma. You may see other characters, they are based on your regional settings.
Step 2 - Compare dates to end date ranges
The less than and equal sign combined lets you compare dates in B3:B10 to H3:H5, the result is either TRUE or FALSE.
B3:B10<=TRANSPOSE(H3:H5)
becomes
B3:B10<={42826, 42979, 43070}
becomes
{43015; 43065; 42909; 42767; 42951; 42858; 42816; 43069}<={42826, 42979, 43070}
and returns
{FALSE, FALSE, TRUE; FALSE, FALSE, TRUE; FALSE, TRUE, TRUE; TRUE, TRUE, TRUE; FALSE, TRUE, TRUE; FALSE, TRUE, TRUE; TRUE, TRUE, TRUE; FALSE, FALSE, TRUE}.
Notice that the delimiting character is ; in the first array and , in the second array. This will compare vertical dates to horizontal dates and the result is a table.
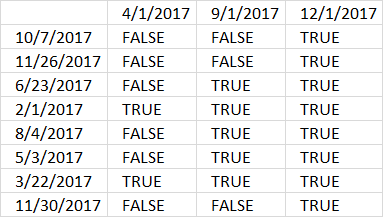
Step 3 - Compare dates to start date ranges
We can use the exact same technique described above in step 2 to compare dates with start dates.
B3:B10>=TRANSPOSE($G$3:$G$5)
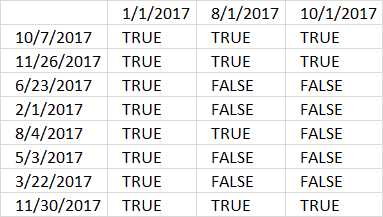
The horizontal dates are now start dates.
Step 4 - Multiply arrays
Both calculated boolean values must be TRUE to match a date range, we can use the asterisk character to multiply the arrays.
The result is always 1 or 0 (zero) when you multiply boolean values. 1 is the numerical equivalent to TRUE and 0 (zero) is FALSE.
(B3:B10<=TRANSPOSE(H3:H5))*(B3:B10>=TRANSPOSE(G3:G5))
The parentheses let you control the order of calculations, we must multiply after the comparisons are made.
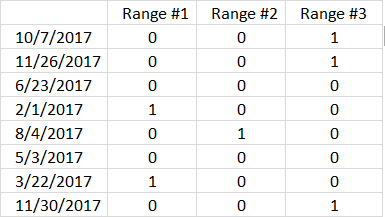
Step 5 - Multiply array with numbers
We now know which range each date belongs to, however, you may have noticed that some dates have no date range.
(B3:B10<=TRANSPOSE(H3:H5))*(B3:B10>=TRANSPOSE(G3:G5))*C3:C10
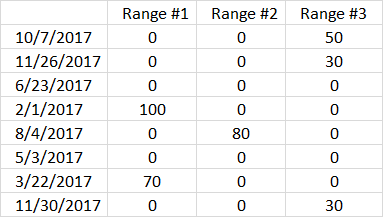
Step 6 - Sum numbers in array
The SUMPRODUCT function adds the numbers and returns a total.
SUMPRODUCT((B3:B10<=TRANSPOSE(H3:H5))*(B3:B10>=TRANSPOSE(G3:G5))*C3:C10)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0, 0, 50; 0, 0, 30; 0, 0, 0; 100, 0, 0; 0, 80, 0; 0, 0, 0; 70, 0, 0; 0, 0, 30})
and returns 360 in cell H10.

The following formula returns the corresponding date range number, this lets you quickly note which date range a date belongs to.
Formula in cell D3:
22. Sum based on currency rates
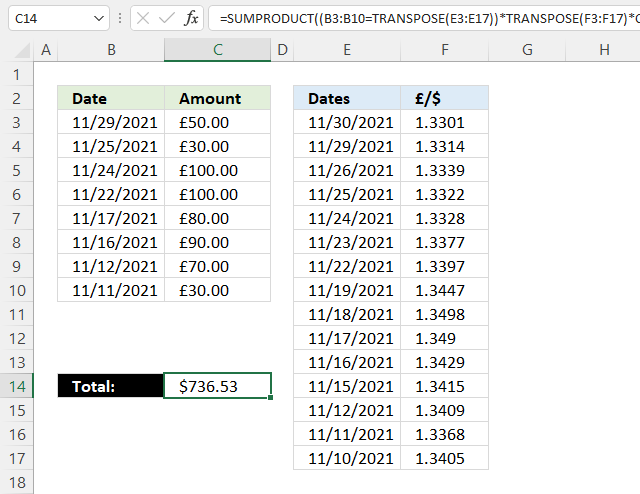
Formula in cell C14:
22.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Rearrange values
The TRANSPOSE function rearranges values from horizontal to vertical or vice versa.
TRANSPOSE(array)
TRANSPOSE(E3:E17)
becomes
TRANSPOSE({44530; 44529; 44526; 44525; 44524; 44523; 44522; 44519; 44518; 44517; 44516; 44515; 44512; 44511; 44510})
and returns
{44530, 44529, 44526, 44525, 44524, 44523, 44522, 44519, 44518, 44517, 44516, 44515, 44512, 44511, 44510}.
Step 2 - Compare values
The equal sign lets you compare values, TRUE if identical (not case sensitive) and FALSE if not.
B3:B10=TRANSPOSE(E3:E17)
becomes
B3:B10={44530, 44529, 44526, 44525, 44524, 44523, 44522, 44519, 44518, 44517, 44516, 44515, 44512, 44511, 44510}
becomes
{44529; 44525; 44524; 44522; 44517; 44516;44512;44511}={44530, 44529, 44526, 44525, 44524, 44523, 44522, 44519, 44518, 44517, 44516, 44515, 44512, 44511, 44510}
and returns
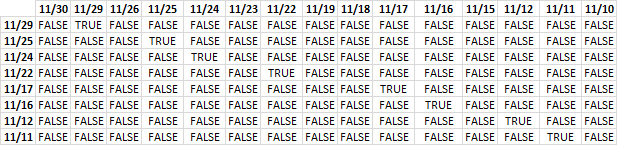
The image above shows the array containing the boolean values TRUE or FALSE, currency dates are above the array arranged horizontally. The other dates are arranged vertically and located to the left of the array.
Step 3 - Multiply with currency data
(B3:B10=TRANSPOSE(E3:E17))*TRANSPOSE(F3:F17)
returns
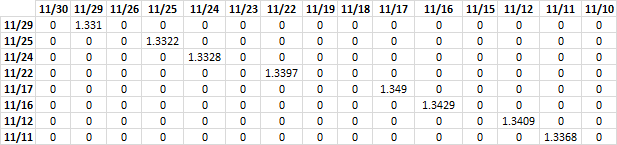
FALSE * currency_data = 0 (zero)
TRUE * currency_data = currency_data
The array contains the corresponding currency rate if the dates match. If dates don't match 0 (zero) is returned.
Step 4 - Multiply with amounts
(B3:B10=TRANSPOSE(E3:E17))*TRANSPOSE(F3:F17)*C3:C10
returns
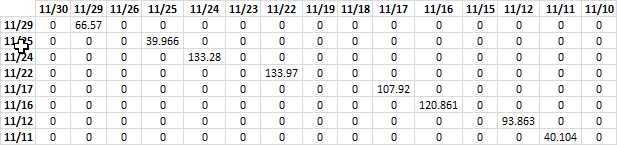
Step 5 - Sum numbers
The SUMPRODUCT function adds the numbers and returns a total.
SUMPRODUCT((B3:B10=TRANSPOSE(E3:E17))*TRANSPOSE(F3:F17)*C3:C10)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0, 66.57, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 39.966, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 133.28, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 133.97, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 107.92, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 120.861, 0, 0, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 93.863, 0, 0;0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 40.104, 0})
and returns 736.53 in cell C14.

23. Get Excel *.xlsx
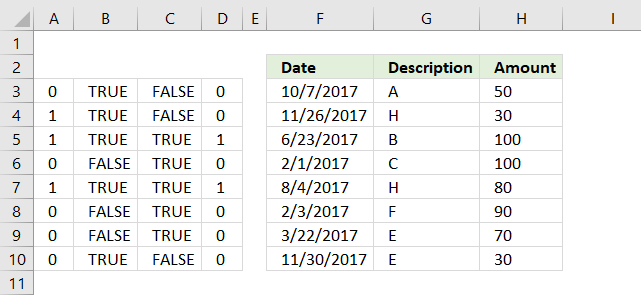
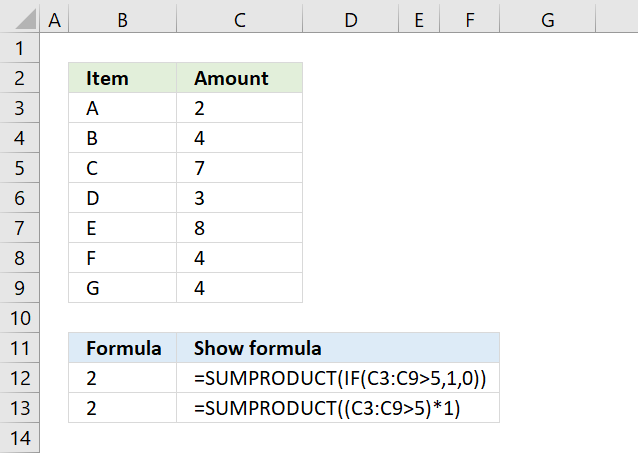
24. Simplify IF functions
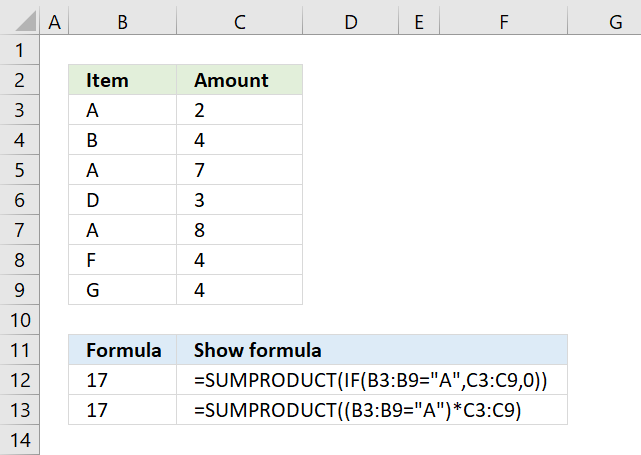
The first argument in the IF function is a logical expression, use that in your SUMPRODUCT formula. The formula in B13 does the same thing as in B12.
You need to tell Excel the order of calculation, in other words, make sure you calculate C3:C9>5 before you multiply by 1. To do that use parentheses.
The larger than comparison operator compares each value in C3:C9 if larger than 5. It returns an array the same size as C3:C9 containing boolean values, TRUE or FALSE.
The picture above shows the array in column D, value 7 and 8 are larger than 5.
The SUMPRODUCT function can't sum boolean values so multiply (using the asterisk *) the logical expression by 1 to convert the boolean values (TRUE and FALSE) to numbers (1 or 0).
The asterisk also has another advantage, you can enter the SUMPRODUCT formula as a regular formula.
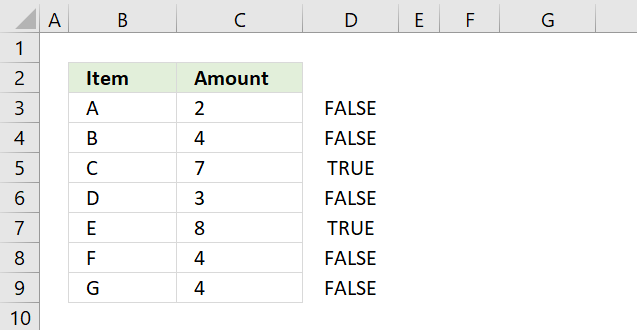
24.1 Combine SUMPRODUCT and IF
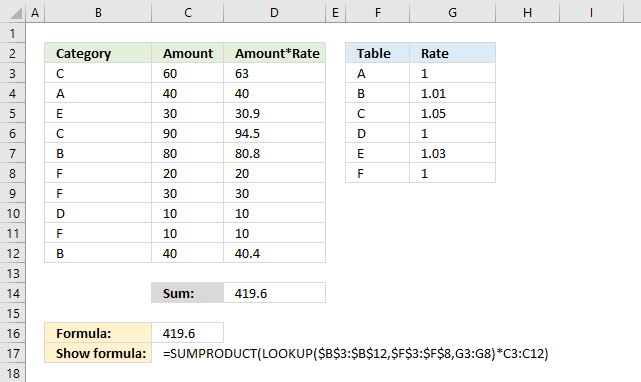
The picture above demonstrates an IF function that checks if a condition is met and if TRUE returns a value in a corresponding cell.
There is no need for the IF function in the above example, simply use the logical expression and multiply with the values you want to use, demonstrated in cell B13.
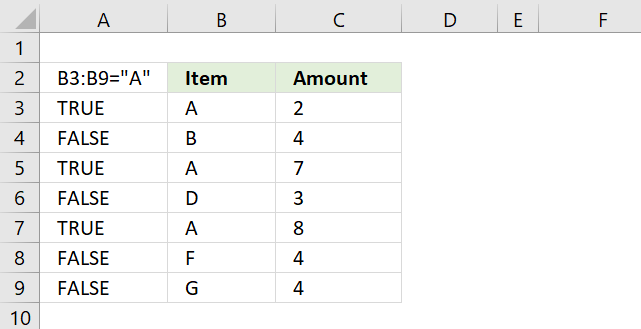
B3:B9="A" returns {TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE} displayed in column A in image above.
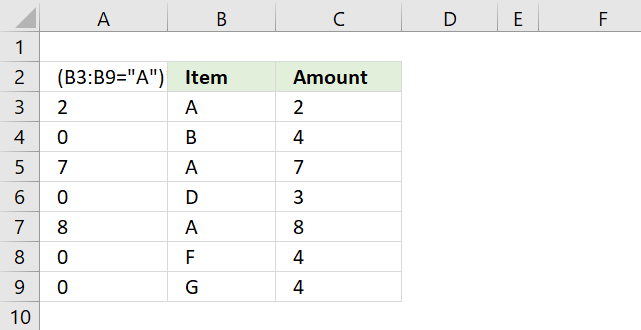
(B3:B9="A")*C3:C9 returns this array: {2;0;7;0;8;0;0} shown in column A.
Lastly, the SUMPRODUCT function sums all the numbers in the array returning 17 in cell B12.
2 + 7 + 8 = 17.
25. If greater than 0 (zero)
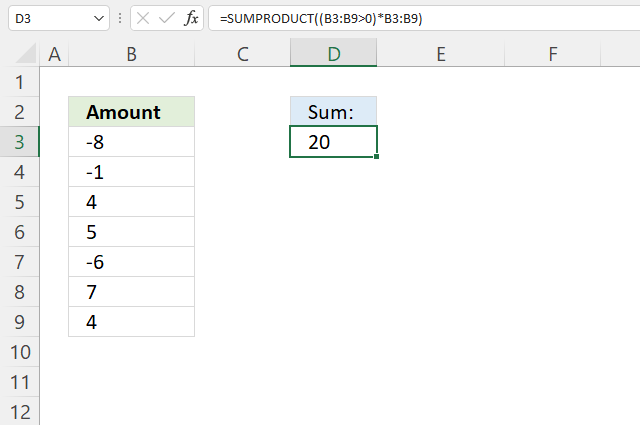
The formula in cell D3 adds numbers from B3:B9 if they are larger than 0 (zero) and returns a total.
Formula in cell D3:
=SUMPRODUCT((B3:B9>0)*B3:B9)
25.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Check if values are larger than 0 (zero)
The larger than sign is a boolean operator that compares values to a condition, it returns TRUE or FALSE based on the outcome.
B3:B9>0 returns {FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 2 - Multiply boolean values with numbers
The parentheses let you control the order of calculation, we must do the comparisons before we multiply.
The asterisk character lets you multiply a value with another value, in this case, with a boolean value.
TRUE is equal to 1 and FALSE is equal to 0 (zero), this will create the following outcomes:
TRUE * number = number
FALSE * number = 0 (zero)
(B3:B9>0)*B3:B9 returns {0; 0; 4; 5; 0; 7; 4}.
Notice how all the negative numbers are converted to 0's (zeros).
Step 3 - Add numbers and return total
The SUMPRODUCT function calculates the product of corresponding values and then returns the sum of each multiplication.
SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
SUMPRODUCT((B3:B9>0)*B3:B9)
becomes
SUMPRODUCT({0; 0; 4; 5; 0; 7; 4})
and returns 20 in cell D3.

26. If between two dates
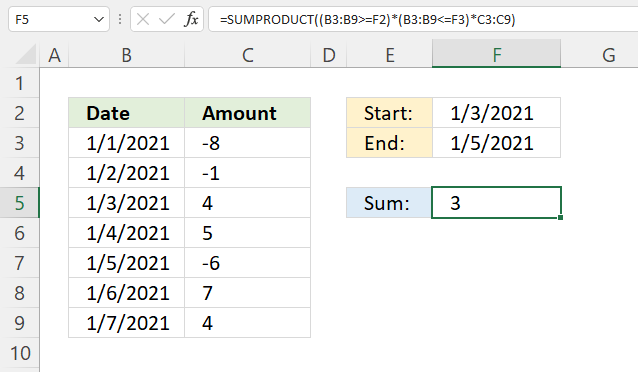
The SUMPRODUCT function shown in cell F5 calculates a total based on two dates. The example above demonstrates the start date in F2 and end date in F3, cells B5, B6, and B7 have dates that match the date range.
The corresponding numbers are in cells C5, C6, and C7. The total is calculated like this 4 + 5 - 6 equals 3.
Formula in cell f5:
26.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Check which dates are equal to or later than the start date
The larger than and the equal signs are boolean operators that compare values to a condition, it returns TRUE or FALSE based on the outcome.
B3:B9>=F2
returns {FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE}.
Step 2 - Check which dates are equal to or earlier than the end date
The less than and the equal signs are boolean operators that compare values to a condition, it returns TRUE or FALSE based on the outcome.
B3:B9<=F3 returns {TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE}.
Step 3 - Multiply arrays
The asterisk character lets you multiply values, this works fine with boolean values as well. This means that you can apply AND logic between the arrays.
TRUE*TRUE = 1
TRUE*FALSE = 0 (zero)
FALSE*TRUE= 0 (zero)
FALSE*FALSE= 0 (zero)
(B3:B9>=F2)*(B3:B9<=F3) returns {0; 0; 1; 1; 1; 0; 0}.
Step 4 - Multiply array with numbers
(B3:B9>=F2)*(B3:B9<=F3)*C3:C9 returns {0; 0; 4; 5; -6; 0; 0}.
Step 5 - Add numbers and return a total
The SUMPRODUCT function calculates the product of corresponding values and then returns the sum of each multiplication.
SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2], ...)
SUMPRODUCT((B3:B9>=F2)*(B3:B9<=F3)*C3:C9) returns 3 in cell F5. 4 + 5 - 6 = 3
27. If cell contains text
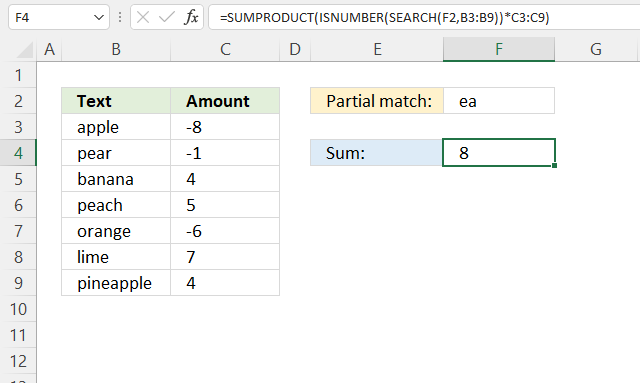
The SUMPRODUCT function displayed in cell F4 calculates a total based on a string specified in cell F2. If a cell in B3:B9 contains the string (partial match) the corresponding number in cell C3:C9 is added to a total.
The image above demonstrates that the string is found in cells B4, B6, and B9. The corresponding cells in column C are C4, C6, and C9. The total is calculated like this: -1 + 5 + 4 equals 8.
Formula in cell F4:
=SUMPRODUCT(ISNUMBER(SEARCH(F2, B3:B9))*C3:C9)
27.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Find cells containing the string
The SEARCH function returns a number representing the position of character at which a specific text string is found reading left to right. It is not a case-sensitive search.
SEARCH(find_text,within_text, [start_num])
SEARCH(F2, B3:B9) returns {#VALUE!; 2; #VALUE!; 2; #VALUE!; #VALUE!; 4}.
The SEARCH function returns an error value if the string is not found.
Step 2 - Convert result to boolean values
The error values break the formula, we need to take care of possible error values.
The ISNUMBER function checks if a value is a number, returns TRUE or FALSE. This works fine with error values as well.
ISNUMBER(value)
ISNUMBER(SEARCH(F2, B3:B9)) returns {FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}.
Notice that the error values are now boolean value FALSE.
Step 3 - Multiply with numbers
Boolean values can be used in multiplication, TRUE has the numerical equivalent of 1 and FALSE is 0 (zero).
TRUE * number = number
FALSE * number = 0 (zero)
ISNUMBER(SEARCH(F2, B3:B9))*C3:C9 returns {0; -1; 0; 5; 0; 0; 4}.
Step 4 - Add values and return total
SUMPRODUCT(ISNUMBER(SEARCH(F2, B3:B9))*C3:C9)
28. If or
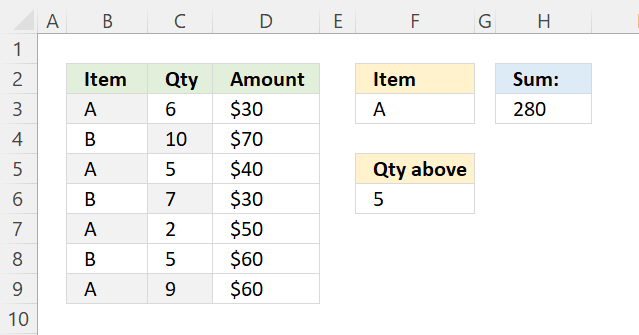
The SUMPRODUCT function in cell H3 adds numbers from D3:D9 if the corresponding cell in B3:B9 equals the value in cell F3 or C3:C9 is above the value specified in cell F6.
Formula in cell H3:
28.1 Explaining formula
Step 1 - Evaluate condition
The equal sign compares value to value, however, not considering upper and lower cases. You need the EXACT function to do that.
B3:B9=F3 returns {TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE}.
Step 2 - Check if the number is larger than the condition
The larger than sign compares C3:C9 to number in F6, the result is a boolean value TRUE or FALSE.
C3:C9>F6 returns {TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE}.
Step 3 - Perform OR logic between arrays
The plus sign adds value to value, this applies OR logic between the arrays.
TRUE + TRUE = 1
TRUE + FALSE = 1
FALSE + TRUE = 1
FALSE + FALSE = 0 (zero)
This means that at least one condition must be met.
(B3:B9=F3) + (C3:C9>F6) equals {2; 1; 1; 1; 1; 0; 2}.
In Excel, any other number than 0 (zero) is considered to be TRUE even negative numbers. FALSE is 0 (zero).
Step 4 - Check if values in array are larger than 0 (zero)
((B3:B9=F3)+(C3:C9>F6))>0 returns {TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE}.
Step 5 - Multiply with numbers
(((B3:B9=F3)+(C3:C9>F6))>0)*D3:D9 returns {30; 70; 40; 30; 50; 0; 60}.
Step 6 - Sum numbers in array
SUMPRODUCT((((B3:B9=F3)+(C3:C9>F6))>0)*D3:D9) returns 280 in cell H3.
Get Excel *.xlsx file
'SUMPRODUCT' function examples
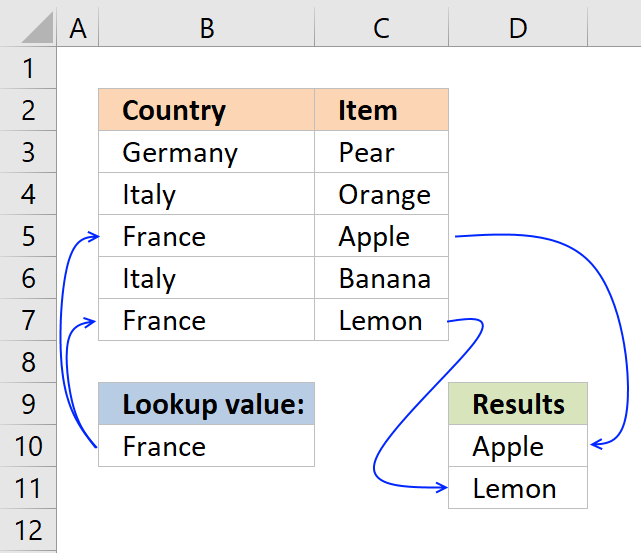
This post explains how to lookup a value and return multiple values. No array formula required.
Table of Contents Automate net asset value (NAV) calculation on your stock portfolio Calculate your stock portfolio performance with Net […]
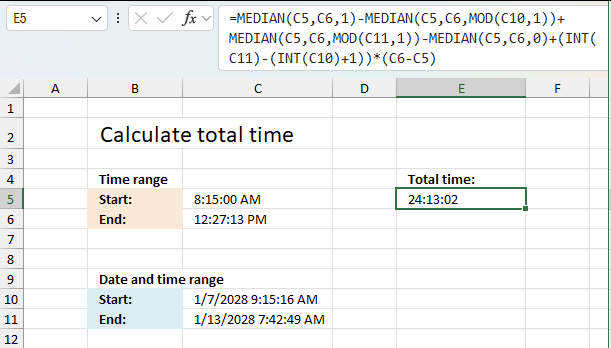
This article explains how to calculate an overlapping time ranges across multiple days. This can be very useful in situations […]
Functions in 'Math and trigonometry' category
The SUMPRODUCT function function is one of 62 functions in the 'Math and trigonometry' category.
Excel function categories
Excel categories
12 Responses to “How to use the SUMPRODUCT function”
Leave a Reply
How to comment
How to add a formula to your comment
<code>Insert your formula here.</code>
Convert less than and larger than signs
Use html character entities instead of less than and larger than signs.
< becomes < and > becomes >
How to add VBA code to your comment
[vb 1="vbnet" language=","]
Put your VBA code here.
[/vb]
How to add a picture to your comment:
Upload picture to postimage.org or imgur
Paste image link to your comment.
This can be solved without using array in the same fashion (makes the file much lighter when compared to array) =sumproduct((logical test on array1)*(logical test on array2)*...*(result array))
Vipul,
Thanks!
Formula in C26:
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(B20:B25, Model)*COUNTIF(C20:C25, Country)*COUNTIF(D20:D25, Plane)*Amount) + Enter
Hi Oscar,
While reading this article "How to use excel SUMPRODUCT function" I detected what I think is a minor error.
In example 3 (The California-Los angeles example), you say that the formula transaltes to:
=({FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE})*({FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE})*{10; 20; 40; 10; 20; 30; 10}
but i think that the second set of boolean values is not correct and should be:
=({FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE})*({FALSE; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE; TRUE; FALSE})*{10; 20; 40; 10; 20; 30; 10}
Is that correct or I understood incorrectly?
Thanks in advance for your support with this blog.
Regards
Arturo
Arturo,
thanks!!
As alternative solution in cell C18 you can write the formula
=SUM(C3:C17)/2miho66,
Yes, you are right. A lot easier, thanks for commenting.
Another complete this task:
after use autosum, select again whole range (C3:F17) and use Find&Replace to replace sting "sum(" with "subtotal(9,"
Ciprian Stoian,
Yes, you are right. The SUBTOTAL function ignores other SUBTOTALS to avoid double counting.
Thank you for commenting.
I don't understand why do you say „Use asterisks between logical expressions instead of commas and you don't need to enter the SUMPRODUCT function as an array formula.”
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(G2:G3,C3:C10),--(G5=B3:B10),D3:D10)works fine and isn't an array formula...something is wrong with autoformatting.
The formula is:
SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(G2:G3,C3:C10),--(G5=B3:B10),D3:D10)
Ciprian Stoian
I believe SUMPRODUCT in earlier Excel versions had to be entered as an array formula in some cases in order to work. The asterisk made it possible to enter the formula as a regular formula.
This seems to have changed in Excel 365, thanks for pointing it out.
please help to generate formula. i need to look if the currency is the same and calculate the exchange rates according to the date range.
Exchange Rates From To EUR GBP USD
Jan 01/01/2019 31/01/2019 1.00 1.055 0.832
Feb 01/02/2019 28/02/2019 1.00 1.097 0.834
Mar 01/03/2019 31/03/2019 1.00 1.094 0.838
Apr 01/04/2019 30/04/2019 1.00 1.113 0.842
May 01/05/2019 31/05/2019 1.00 1.099 0.845
Customer account Invoice Tour id Date Departure date Amount currency VAT amount Net amount Currency Voucher
C000002475 CI17182289 E08205231 01/01/2019 01/01/2019 292.66 0 292.66 EUR CI17182289
C000002475 CI17228471 T02200223 17/01/2019 17/01/2019 136.26 0 136.26 EUR CI17228471
C000002475 CI17231407 T02200224 18/01/2019 18/01/2019 280.32 0 280.32 EUR CI17231407