How to use DIALOG BOXES
A dialog box is an excellent alternative to a userform, they are built-in to VBA and can save you time because you don't need to code and build a userform. Some of these dialog boxes also have built-in validation. This article shows you what you can and can't do with dialog boxes.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- How to create a Message box (VBA)
- Input box (vba)
- Input box (Excel)
- DataForm
- FileDialog
- GetOpenFilename
- GetSaveAsFilename
1. Introduction
- What is VBA?
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language created by Microsoft that is used for automating tasks in Microsoft Office applications such as Excel, Word, and Access. It allows users to create macros which can automate repetitive tasks and enhance Office functionality with custom-made code. - What is a dialog box?
A dialog box is a small window that appears on the screen to communicate information to the user or request input. It typically requires user interaction before continuing with the program. Examples include message boxes, input boxes, and custom user forms.
- What is a message box?
A message box in VBA (MsgBox) is a pop-up dialog that displays a message to the user. It can include buttons (e.g., OK, Yes, No, Cancel) and icons (e.g., information, warning, error). It is commonly used to provide information, warnings, or to get simple user confirmations.
- What is an input box?
An input box (InputBox) is a built-in function in VBA that prompts the user to enter a value. It returns the entered value as a string.
- What is the difference between an input box in Excel and VBA?
- Excel Input box
- Used for user-friendly data entry in cells
- Displays a small pop-up tooltip near a cell
- Limited customization (only text hints)
- Does not require VBA
- VBA Input Box (InputBox function)
- Used in VBA to get user input during macro execution
- Displays a separate dialog box
- Fully customizable (can change title, prompt, default value)
- Requires VBA code to display and process input
- Excel Input box
- What is a data form?
A data form in Excel is a built-in tool that provides a simple interface for entering, viewing, and editing records in a structured table. It allows users to navigate records one by one and enter data without directly modifying the spreadsheet. Data forms are useful when handling small databases but are limited compared to full-fledged VBA user forms, which offer more flexibility and control.
2. How to create a Message box (VBA)
The most basic dialog box you probably have seen many times is the message box. In its most simple form, it gives the user a message you specify and an OK button.
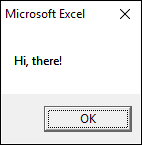
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Hi, there!" End Sub
It is a great tool for quickly troubleshooting a subroutine or a custom function. The message box has more options than displaying text or variables, these are the arguments:
2.1 Message box arguments

Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKOnly, "This is a title" End Sub
Prompt - Text shown in message box
Buttons - You can select of a variety of different buttons and icons. If you can't find the buttons you need, a user form is required.
vbOKOnly - 0
vbOKCancel - 1
vbAbortRetryIgnore - 2
vbYesNoCancel - 3
vbYesNo - 4
vbRetryCancel - 5
vbCritical - 16
vbQuestion - 32
vbExclamation - 48
vbInformation - 64
vbDefaultButton1 - 0
vbDefaultButton2 - 256
vbDefaultButton3 - 512
vbDefaultButton4 - 768
Title - Text at the very top of the message box. (Optional)
Helpfile - Path to your helpfile. (Optional)
Context - A numerical expression. (Optional, required if you specify a helpfile)
2.2 How to configure buttons on a message box
There are six different button setups. The most basic message box shows a text string or a variable and an OK button.
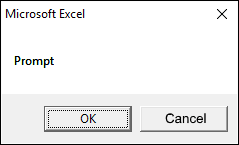
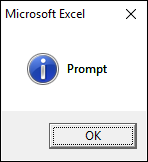
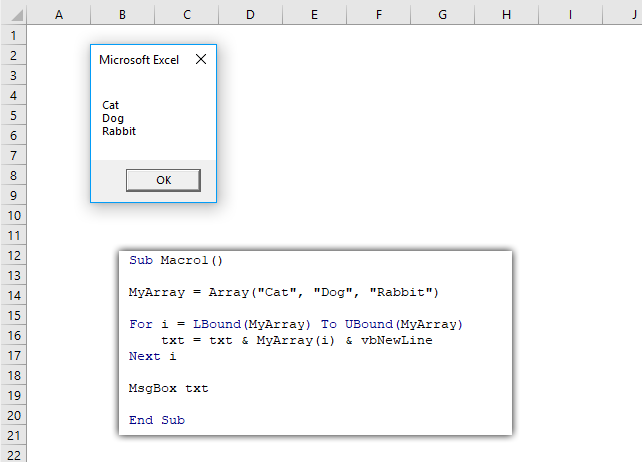
2.2.1 vbOKOnly
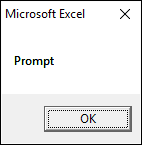
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a single "OK" button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKOnly End Sub
You don't even need to specify the vbOKOnly argument to show the above dialog box.
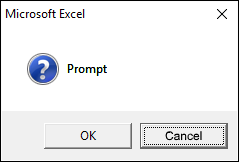
2.2.2 vbOKCancel
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows an "OK" and "Cancel" button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbOKCancel argument displays OK and Cancel buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel End Sub
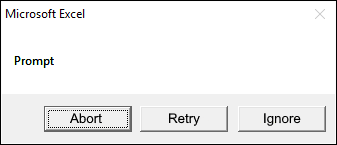
2.2.3 vbAbortRetryIgnore
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows an "Abort", "Retry", and "Ignore" button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbAbortRetryIgnore argument shows three buttons, abort, retry and ignore on the dialog box.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbAbortRetryIgnore End Sub
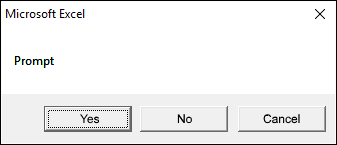
2.2.4 vbYesNoCancel
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a "Yes", "No", and "Cancel" button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbYesNoCancel argument also shows three buttons, however, they are named, Yes, No, and Cancel.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbYesNoCancel End Sub
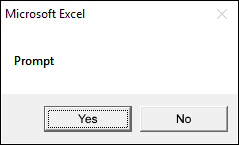
2.2.5 vbYesNo
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a "Yes" and "No" button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbYesNo argument diplays Yes and No buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbYesNo End Sub
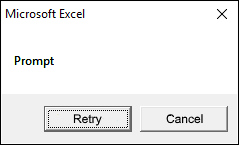
2.2.6 vbRetryCancel
vbRetryCancel argument shows Retry and Cancel buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbRetryCancel End Sub
2.3 Icons
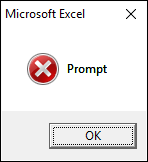
2.3.1 vbCritical
vbCritical shows this icon on the message box, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbCritical End Sub
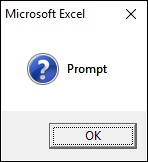
2.3.2 vbQuestion
vbQuestion shows this query icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbQuestion End Sub
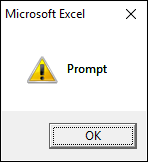
2.3.3 vbExclamation
vbExclamation shows a warning icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbExclamation End Sub
2.3.4 vbinformation
vbinformation shows an information icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbInformation End Sub
2.3 Combine buttons and icons
If you look at the message box arguments at the beginning of this post, you will see a number next to each constant. Combining for example an OK and Cancel button with a query icon you simply add the numbers for those constants. OK and Cancel has value 1 and the query icon has value 32.
1 + 32 = 33
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", 33 End Sub
You can combine constants intead of values, if you prefer that. See macro below, it produces the same result as the macro above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion End Sub
2.4 Default buttons
You can change the default button for a message box, see the arguments in the beginning of this post. The following message box has the OK button as the default button, it has a dotted line around the text "OK".
You can change it to the second button by adding 256 to the second argument. 33 + 256 = 289
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", 289 End Sub
If you prefer you can add the constants to the second argument, as well. This macro shows the same message box as above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton2 End Sub
2.5 Messagebox return value
The message box returns one of these values depending on which button was press with left mouse button oned on by the user.
vbOK - 1
vbCancel - 2
vbAbort - 3
vbRetry - 4
vbIgnore - 5
vbYes - 6
vbNo - 7
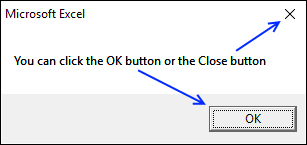
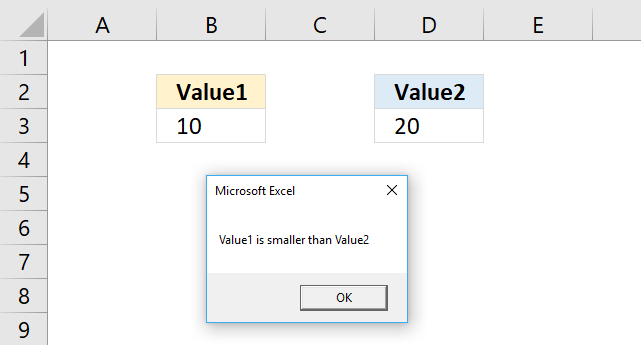
This message box allows you to press with left mouse button on the OK button or the Close button. Both buttons result in the value 1 or vbOK.
Sub Macro1()
Dim btt
btt = MsgBox("You can press with left mouse button on the OK button or the Close button", vbOKOnly)
MsgBox btt
End Sub
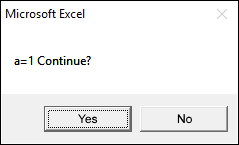
The following macro allows you to continue or stop a loop using a message box. If you press with left mouse button on No the macro ends.
Sub Macro1()
Dim a As Integer
For a = 1 To 10
If MsgBox("a=" & a & " Continue?", vbYesNo) = vbNo Then Exit For
Next a
End Sub
2.6 Help file
Here is an example of how to use a msgbox with a helpfile.
<href="https://www.get-digital-help.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/dialog-boxes-help-file-1.png">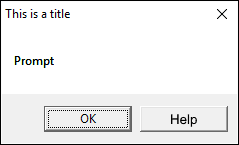
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbMsgBoxHelpButton, "This is a title", "c:\temp\helpfile.chm", 7 End Sub
2.7 Working with text in a message box
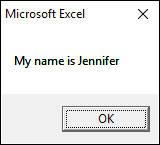
The following macro shows you how to concatenate text and a variable.
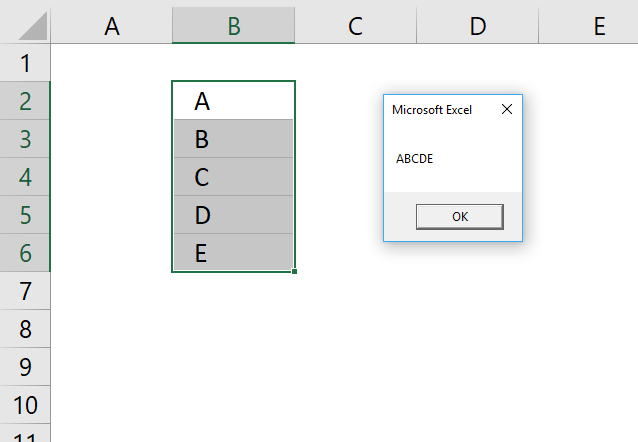
Sub Macro1() Dim nm As String nm = "Jennifer" MsgBox "My name is " & nm End Sub
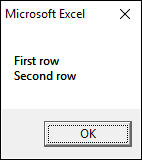
This macro shows you how to put text on two rows.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "First row" & vbNewLine & "Second row" End Sub
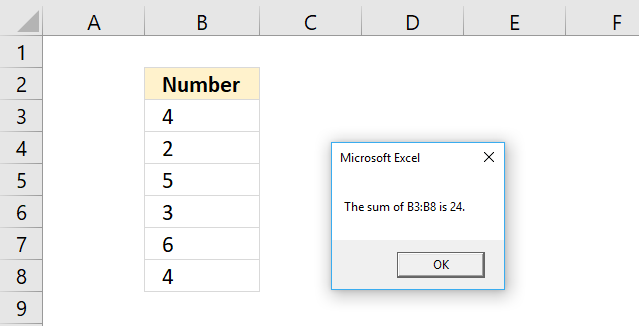
You can also show data with a delimiting tab.
Sub Macro1() Dim a As Integer, result As String For a = 1 To 8 result = result & a & vbTab Next a MsgBox result End Sub
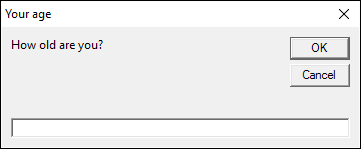
3. Input box (VBA)
An input box asks the user for a value, you can specify the text and the title in the inputbox. You also have the option where to show the input box on screen and a default input value.
prompt - text in input box
title - Text at the very top of the input box
default - default value shown in the input box
xpo,ypos - specify where you want the input box on the screen from the upper-left corner.
helpfile - path to help file
context - A numerical value
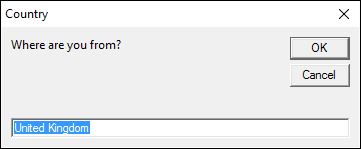
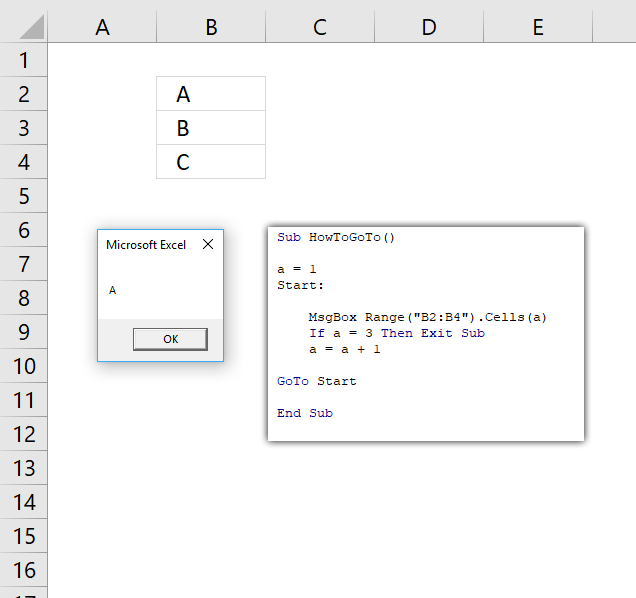
3.1 How to set the default value for an input box?
This macro asks where you are from. The default value is "United Kingdom".
Sub Macro1()
Dim Country
Country = InputBox("Where are you from?", "Country", "United Kingdom")
MsgBox Country
End Sub
Note, the Input box returns nothing if you press with left mouse button on the Cancel button.
4. Input box (Excel)
Excel input box is more versatile, it will do basic validation for you and the user can select a cell range on a worksheet. You have also the option to select one or multiple data types returned by the input box.
prompt - text in input box
title - Text at the very top of the input box
default - default value shown in the input box
left, top - specify where you want the input box from the upper-left corner of the screen.
helpfile - path to help file
HelpContextID - A numerical value
Type - A number representing the data type returned
0 - Formula
1 - Number
2 - Text
4 - Logical value, True or False
8 - A cell reference
16 - Error value
64 - An array of values
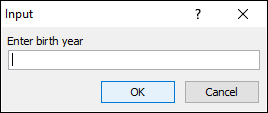
4.1 Number
Sub Macro1()
Dim cd
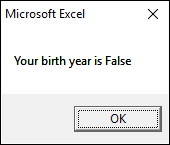
cd = Application.InputBox("Enter birth year", , , , , , , 1)
MsgBox "Your birth year is " & cd
End Sub
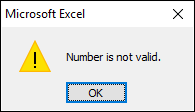
Excel provides basic data validation, if you type a text string excel gives you this warning message.
If you press with left mouse button on "Cancel" button excel returns "False".
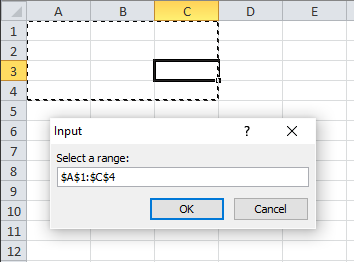
4.2 Range
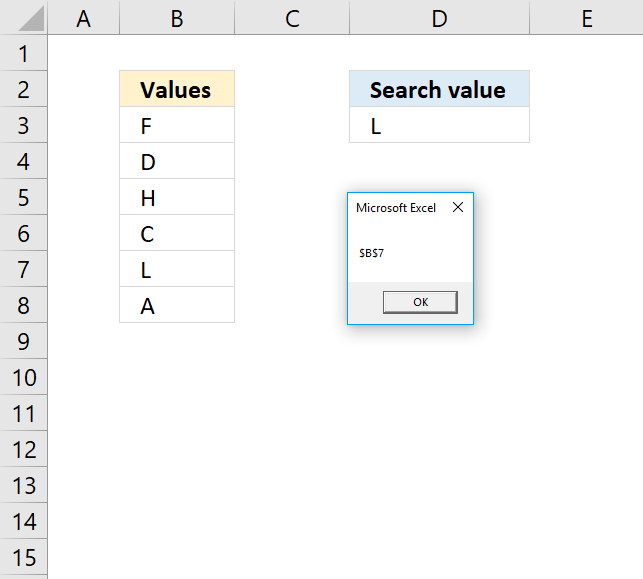
Data type 8 (Cell reference) lets the user select a cell range.
Sub Macro1()
Dim rngAs Range
Set rng = Application.InputBox("Select a range: ", , , , , , , 8)
MsgBox "You selected " & rng.Address
End Sub
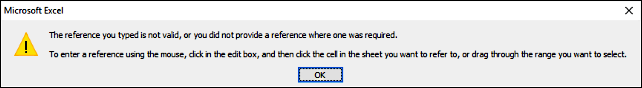
If the user enters something else than a cell reference excel gives this message until a valid cell reference is entered:
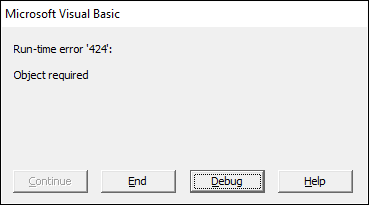
Press with left mouse button oning on "Cancel" button makes excel error out:
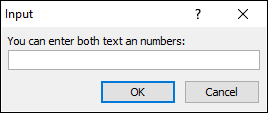
4.3 Combine data types
If you combine data types by adding their corresponding value, like this 1+2 = 3 the user is allowed to enter both numbers and text.
Sub Macro1()
Dim cd
cd = Application.InputBox("You can enter both text an numbers: ", , , , , , , 3)
MsgBox "You entered " & cd
End Sub
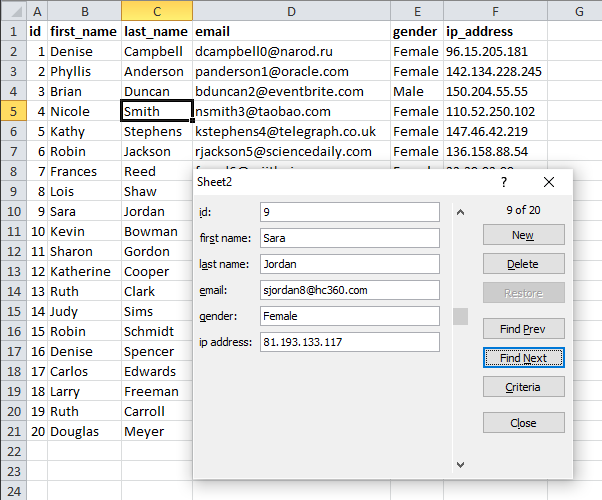
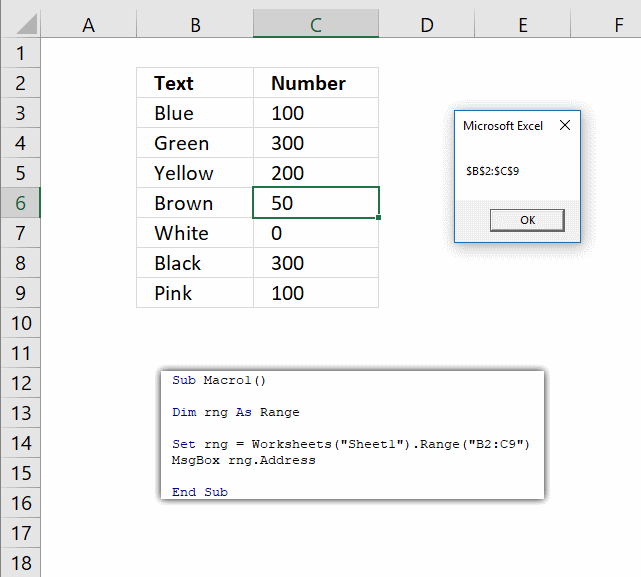
5. Data Form
Data in this table is made up and random.
The data form is a smart dialog box, it analyzes your table and customizes the dialog box using table headers.
Make sure you have a cell selected in the table you want to work with before running this macro:
Sub Macro1() ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub
6. FileDialog
FileDialog property lets you prompt the user for a directory or open/save/select a file
fileDialogType - Choose between 4 constants, see below.
msoFileDialogFilePicker - Select a file
msoFileDialogFolderPicker - Select a folder
msoFileDialogOpen - Open a file
msoFileDialogSaveAs - Save a file
6.1 msoFileDialogFilePicker
Allows the user to select a file. The following macro prompts the user for a file o multiple files and then a message box returns the path and file name for each file.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker) .Show For i = 1 To .SelectedItems.Count MsgBox .SelectedItems(i) Next i End With End Sub
6.2 msoFileDialogFolderPicker
The following macro lets the user pick a folder. A message box displays the path and folder name.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
6.3 msoFileDialogOpen
The macro below asks the user for a file to open. A message box displays the path and file name. Note, it doesn't open the file.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
6.4 msoFileDialogSaveAs
This macro lets the user pick a folder and a save name. A message box displays the path and file name. It doesn't save the file
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
7. GetOpenFilename
Filefilter - Filter criteria (Optional)
FilterIndex - Index number of default filter (Optional)
Title - title of dialog box (Optional)
Multiselect - Enables the user to select multiple filenames (Optional)
The following macro asks for a file to open, filters used are *.xlsx and *.xlsm. The second filter is the default value. Keep in mind, the macro doesn't open the file it just returns a file name and path.
Sub Macro1()
Dim txt
txt = Application.GetOpenFilename("Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx, Excel macro files (*.xlsm),*.xlsm", 2)
MsgBox txt
End Sub
If the user press with left mouse button ons "Cancel" a False is returned.
8. GetSaveFilename
Filefilter - Filter criteria (Optional)
FilterIndex - Index number of default filter (Optional)
Title - title of dialog box (Optional)
Sub Macro1()
Dim txt
txt = Application.GetSaveAsFilename("Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx, Excel macro files (*.xlsm),*.xlsm", 2)
MsgBox txt
End Sub
This macro does not save the file, it only returns the selected path and name.
Macro category
Table of Contents How to create an interactive Excel chart How to filter chart data How to build an interactive […]
Table of Contents Excel monthly calendar - VBA Calendar Drop down lists Headers Calculating dates (formula) Conditional formatting Today Dates […]
Table of Contents Split data across multiple sheets - VBA Add values to worksheets based on a condition - VBA […]





How to comment
How to add a formula to your comment
<code>Insert your formula here.</code>
Convert less than and larger than signs
Use html character entities instead of less than and larger than signs.
< becomes < and > becomes >
How to add VBA code to your comment
[vb 1="vbnet" language=","]
Put your VBA code here.
[/vb]
How to add a picture to your comment:
Upload picture to postimage.org or imgur
Paste image link to your comment.
Contact Oscar
You can contact me through this contact form